Clinical review of genetic epileptic encephalopathies
- PMID: 22342633
- PMCID: PMC3590070
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejmg.2011.12.010
Clinical review of genetic epileptic encephalopathies
Abstract
Seizures are a frequently encountered finding in patients seen for clinical genetics evaluations. The differential diagnosis for the cause of seizures is quite diverse and complex, and more than half of all epilepsies have been attributed to a genetic cause. Given the complexity of such evaluations, we highlight the more common causes of genetic epileptic encephalopathies and emphasize the usefulness of recent technological advances. The purpose of this review is to serve as a practical guide for clinical geneticists in the evaluation and counseling of patients with genetic epileptic encephalopathies. Common syndromes will be discussed, in addition to specific seizure phenotypes, many of which are refractory to anti-epileptic agents. Divided by etiology, we overview the more common causes of infantile epileptic encephalopathies, channelopathies, syndromic, metabolic, and chromosomal entities. For each condition, we will outline the diagnostic evaluation and discuss effective treatment strategies that should be considered.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Masson SAS. All rights reserved.
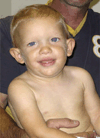
Figures




References
-
- Epilepsy Fast Facts. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Atlanta, GA: US Department of Health and Human Services; 2010.
-
- Pal DK, Pong AW, Chung WK. Genetic evaluation and counseling for epilepsy. Nature reviews. Neurology. 2010;6(8):445–453. - PubMed
-
- Wolff M, Cass-Perrot C, Dravet C. Severe myoclonic epilepsy of infants (Dravet syndrome): natural history and neuropsychological findings. Epilepsia. 2006;47(Suppl. 2):45–48. - PubMed
-
- Gillberg C, et al. Autism associated with marker chromosome. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry. 1991;30(3):489–494. - PubMed
-
- Marini C, et al. SCN1A duplications and deletions detected in Dravet syndrome: implications for molecular diagnosis. Epilepsia. 2009;50(7):1670–1678. - PubMed

