Melanocortin 4 receptor signaling in dopamine 1 receptor neurons is required for procedural memory learning
- PMID: 22342812
- PMCID: PMC3314089
- DOI: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2012.01.025
Melanocortin 4 receptor signaling in dopamine 1 receptor neurons is required for procedural memory learning
Abstract
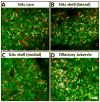
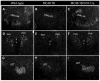
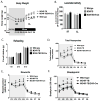
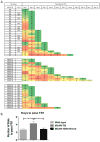
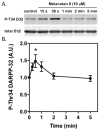
It is now widely recognized that exposure to palatable foods engages reward circuits that promote over-eating and facilitate the development of obesity. While the melanocortin 4 receptor (MC4R) has previously been shown to regulate food intake and energy expenditure, little is known about its role in food reward. We demonstrate that MC4R is co-expressed with the dopamine 1 receptor (D1R) in the ventral striatum. While MC4R-null mice are hyperphagic and obese, they exhibit impairments in acquisition of operant responding for a high fat reinforcement. Restoration of MC4R signaling in D1R neurons normalizes procedural learning without affecting motivation to obtain high fat diet. MC4R signaling in D1R neurons is also required for learning in a non-food-reinforced version of the cued water maze. Finally, MC4R signaling in neostriatal slices increases phosphorylation of the Thr34 residue of DARPP-32, a protein phosphatase-1 inhibitor that regulates synaptic plasticity. These data identify a novel requirement for MC4R signaling in procedural memory learning.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The expression of MC4Rs in D1R neurons regulates food intake and locomotor sensitization to cocaine.Genes Brain Behav. 2013 Aug;12(6):658-65. doi: 10.1111/gbb.12057. Epub 2013 Jul 17. Genes Brain Behav. 2013. PMID: 23786641 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of DARPP-32 phosphorylation by three distinct dopamine D1-like receptor signaling pathways in the neostriatum.J Neurochem. 2008 Nov;107(4):1014-26. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2008.05702.x. Epub 2008 Sep 24. J Neurochem. 2008. PMID: 18823371
-
Nicotine regulates DARPP-32 (dopamine- and cAMP-regulated phosphoprotein of 32 kDa) phosphorylation at multiple sites in neostriatal neurons.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2005 Nov;315(2):872-8. doi: 10.1124/jpet.105.090852. Epub 2005 Jul 22. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2005. PMID: 16040813
-
The Melanocortin System behind the Dysfunctional Eating Behaviors.Nutrients. 2020 Nov 14;12(11):3502. doi: 10.3390/nu12113502. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 33202557 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Understanding melanocortin-4 receptor control of neuronal circuits: Toward novel therapeutics for obesity syndrome.Pharmacol Res. 2018 Mar;129:10-19. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2018.01.004. Epub 2018 Jan 9. Pharmacol Res. 2018. PMID: 29329999 Review.
Cited by
-
The expression of MC4Rs in D1R neurons regulates food intake and locomotor sensitization to cocaine.Genes Brain Behav. 2013 Aug;12(6):658-65. doi: 10.1111/gbb.12057. Epub 2013 Jul 17. Genes Brain Behav. 2013. PMID: 23786641 Free PMC article.
-
Inter-individual variability amplified through breeding reveals control of reward-related action strategies by Melanocortin-4 Receptor in the dorsomedial striatum.Commun Biol. 2022 Feb 8;5(1):116. doi: 10.1038/s42003-022-03043-2. Commun Biol. 2022. PMID: 35136204 Free PMC article.
-
Trk B signaling in dopamine 1 receptor neurons regulates food intake and body weight.Obesity (Silver Spring). 2013 Nov;21(11):2372-6. doi: 10.1002/oby.20382. Epub 2013 May 31. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2013. PMID: 23512795 Free PMC article.
-
Association between MC4R rs17782313 polymorphism and overeating behaviors.Int J Obes (Lond). 2015 Jan;39(1):114-20. doi: 10.1038/ijo.2014.79. Epub 2014 May 14. Int J Obes (Lond). 2015. PMID: 24827639 Free PMC article.
-
Moderate voluntary exercise attenuates the metabolic syndrome in melanocortin-4 receptor-deficient rats showing central dopaminergic dysregulation.Mol Metab. 2015 Jul 17;4(10):692-705. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2015.07.003. eCollection 2015 Oct. Mol Metab. 2015. PMID: 26500841 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hoebel BG. Brain neurotransmitters in food and drug reward. Am J Clin Nutr. 1985;2:1133–50. - PubMed
-
- Rothwell NJ, Stock MJ. The development of obesity in animals: the role of dietary factors. Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1984;13:437–49. - PubMed
-
- Finlayson G, King N, Blundell JE. Liking vs. wanting food: importance for human appetite control and weight regulation. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2007;31:987–1002. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

