A common variant near the KCNJ2 gene is associated with T-peak to T-end interval
- PMID: 22342860
- PMCID: PMC3690340
- DOI: 10.1016/j.hrthm.2012.02.019
A common variant near the KCNJ2 gene is associated with T-peak to T-end interval
Abstract
Background: T-peak to T-end (TPE) interval on the electrocardiogram is a measure of myocardial dispersion of repolarization and is associated with an increased risk of ventricular arrhythmias. The genetic factors affecting the TPE interval are largely unknown.
Objective: To identify common genetic variants that affect the duration of the TPE interval in the general population.
Methods: We performed a genome-wide association study on 1870 individuals of Finnish origin participating in the Health 2000 Study. The TPE interval was measured from T-peak to T-wave end in leads II, V(2), and V(5) on resting electrocardiograms, and the mean of these TPE intervals was adjusted for age, sex, and Cornell voltage-duration product. We sought replication for a genome-wide significant result in the 3745 subjects from the Framingham Heart Study.
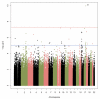
Results: We identified a locus on 17q24 that was associated with the TPE interval. The minor allele of the common variant rs7219669 was associated with a 1.8-ms shortening of the TPE interval (P = 1.1 × 10(-10)). The association was replicated in the Framingham Heart Study (-1.5 ms; P = 1.3 × 10(-4)). The overall effect estimate of rs7219669 in the 2 studies was -1.7 ms (P = 5.7 × 10(-14)). The common variant rs7219669 maps downstream of the KCNJ2 gene, in which rare mutations cause congenital long and short QT syndromes.
Conclusion: The common variant rs7219669 is associated with the TPE interval and is thus a candidate to modify repolarization-related arrhythmia susceptibility in individuals carrying the major allele of this polymorphism.
Copyright © 2012 Heart Rhythm Society. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Common Genetic Variants Modulate the Electrocardiographic Tpeak-to-Tend Interval.Am J Hum Genet. 2020 Jun 4;106(6):764-778. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2020.04.009. Epub 2020 May 7. Am J Hum Genet. 2020. PMID: 32386560 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship of common candidate gene variants to electrocardiographic T-wave peak to T-wave end interval and T-wave morphology parameters.Heart Rhythm. 2010 Jul;7(7):898-903. doi: 10.1016/j.hrthm.2010.03.002. Epub 2010 Mar 4. Heart Rhythm. 2010. PMID: 20215044 Free PMC article.
-
Electrocardiographic transmural dispersion of repolarization in patients with inherited short QT syndrome.Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2008 Jul;13(3):295-300. doi: 10.1111/j.1542-474X.2008.00234.x. Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2008. PMID: 18713331 Free PMC article.
-
Transmural dispersion of repolarization and arrhythmogenicity: the Brugada syndrome versus the long QT syndrome.J Electrocardiol. 1999;32 Suppl:158-65. doi: 10.1016/s0022-0736(99)90074-2. J Electrocardiol. 1999. PMID: 10688320 Review.
-
Classification and Reporting of Potentially Proarrhythmic Common Genetic Variation in Long QT Syndrome Genetic Testing.Circulation. 2018 Feb 6;137(6):619-630. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.030142. Circulation. 2018. PMID: 29431662 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Common Genetic Variants Modulate the Electrocardiographic Tpeak-to-Tend Interval.Am J Hum Genet. 2020 Jun 4;106(6):764-778. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2020.04.009. Epub 2020 May 7. Am J Hum Genet. 2020. PMID: 32386560 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation Between T Peak to End Interval and Left Ventricular Time to Peak Longitudinal Strain in Ischemic Cardiomyopathy Patients.Cardiol Res. 2020 Oct;11(5):337-341. doi: 10.14740/cr1126. Epub 2020 Aug 1. Cardiol Res. 2020. PMID: 32849969 Free PMC article.
-
Twenty-eight genetic loci associated with ST-T-wave amplitudes of the electrocardiogram.Hum Mol Genet. 2016 May 15;25(10):2093-2103. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddw058. Epub 2016 Mar 8. Hum Mol Genet. 2016. PMID: 26962151 Free PMC article.
-
Insight in genome-wide association of metabolite quantitative traits by exome sequence analyses.PLoS Genet. 2015 Jan 8;11(1):e1004835. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004835. eCollection 2015 Jan. PLoS Genet. 2015. PMID: 25569235 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Heroin on Electrocardiographic Parameters.Arq Bras Cardiol. 2020 Dec;115(6):1135-1141. doi: 10.36660/abc.20190296. Arq Bras Cardiol. 2020. PMID: 33470313 Free PMC article. English, Portuguese.
References
-
- Salles GF, Cardoso CR, Leocadio SM, Muxfeldt ES. Recent ventricular repolarization markers in resistant hypertension: are they different from the traditional QT interval? Am J Hypertens. 2008;21:47–53. - PubMed
-
- Oikarinen L, Viitasalo M, Korhonen P, et al. Postmyocardial infarction patients susceptible to ventricular tachycardia show increased T wave dispersion independent of delayed ventricular conduction. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2001;12:1115–20. - PubMed
-
- Viitasalo M, Oikarinen L, Swan H, et al. Ambulatory electrocardiographic evidence of transmural dispersion of repolarization in patients with long-QT syndrome type 1 and 2. Circulation. 2002;106:2473–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources