Diffusion tensor imaging detects axonal injury in a mouse model of repetitive closed-skull traumatic brain injury
- PMID: 22343314
- PMCID: PMC3319388
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neulet.2012.02.024
Diffusion tensor imaging detects axonal injury in a mouse model of repetitive closed-skull traumatic brain injury
Abstract
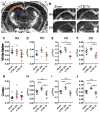
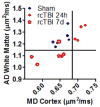
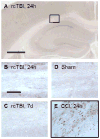
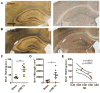
Mild traumatic brain injuries (TBI) are common in athletes, military personnel, and the elderly, and increasing evidence indicates that these injuries have long-term health effects. However, the difficulty in detecting these mild injuries in vivo is a significant impediment to understanding the underlying pathology and treating mild TBI. In the following experiments, we present the results of diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) and histological analysis of a model of mild repetitive closed-skull brain injury in mouse. Histological markers used included silver staining and amyloid precursor protein (APP) immunohistochemistry to detect axonal injury, and Iba-1 immunohistochemistry to assess microglial activation. At 24h post-injury, before silver staining or microglial abnormalities were apparent by histology, no significant changes in any of the DTI parameters were observed within white matter. At 7 days post-injury we observed a reduction in axial and mean diffusivity. Relative anisotropy at 7 days correlated strongly with the degree of silver staining. Interestingly, APP was not observed at any timepoint examined. In addition to the white matter alterations, mean diffusivity was elevated in ipsilateral cortex at 24h but returned to sham levels by 7 days. Altogether, this demonstrates that DTI is a sensitive method for detecting axonal injury despite a lack of conventional APP pathology. Further, this reflects a need to better understand the histological basis for DTI signal changes in mild TBI.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Blumbergs PC, Scott G, Manavis J, Wainwright H, Simpson DA, McLean AJ. Staining of amyloid precursor protein to study axonal damage in mild head injury. Lancet. 1994;344:1055–1056. - PubMed
-
- Geddes JF, Whitwell HL, Graham DI. Traumatic axonal injury: practical issues for diagnosis in medicolegal cases. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2000;26:105–116. - PubMed
-
- Henry LC, Tremblay J, Tremblay S, Lee A, Brun C, Lepore N, Theoret H, Ellemberg D, Lassonde M. Acute and chronic changes in diffusivity measures after sports concussion. J Neurotrauma. 2011;28:2049–2059. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

