Normal myofibrillar development followed by progressive sarcomeric disruption with actin accumulations in a mouse Cfl2 knockout demonstrates requirement of cofilin-2 for muscle maintenance
- PMID: 22343409
- PMCID: PMC3335316
- DOI: 10.1093/hmg/dds053
Normal myofibrillar development followed by progressive sarcomeric disruption with actin accumulations in a mouse Cfl2 knockout demonstrates requirement of cofilin-2 for muscle maintenance
Abstract
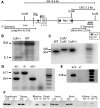
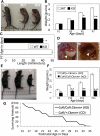
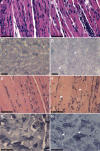
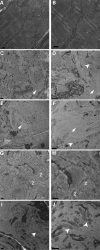
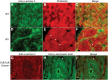
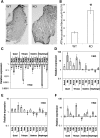
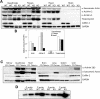
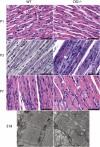
Cofilin-2, a small actin-binding protein and member of the AC protein family that includes cofilin-1 and destrin, is predominantly expressed at sarcomeres in skeletal and cardiac muscles. The role of cofilin-2 in muscle development and function is unclear. In humans, recessive cofilin-2 mutations have been associated with nemaline myopathy with minicores. To investigate the functional role of cofilin-2 in vivo, we generated constitutive and muscle-specific cofilin-2-deficient mice using a cre-loxP strategy. Cofilin-2-deficient mice were similar to their wild-type (WT) littermates at birth, but died by day 8. They were significantly smaller, severely weak and had very little milk in their stomachs. The sarcomeric structure was intact at birth, but by Day 7, skeletal muscles showed severe sarcomeric disruptions starting at the Z-line, along with filamentous actin accumulations consistent with a lack of actin depolymerization activity. Cofilin-2-deficient muscles contained elevated numbers of slow fibers and exhibited upregulation of slow fiber-specific genes. Increased amounts of other sarcomeric proteins including α-actinin-2, α-sarcomeric actin and tropomyosin were also present. While destrin was not expressed in either WT or cofilin-2-deficient muscles, cofilin-1 was similarly expressed in developing myofibers of both genotypes. There was no evidence for compensatory changes in expression of either family member in cofilin-2-deficient tissues. The onset of pathology and weakness in cofilin-2-deficient muscles correlated with normal developmental loss of cofilin-1 expression within myofibers, suggesting that cofilin-1 serves as an early developmental sarcomeric isoform. Overall, cofilin-2, although not critical for muscle development, is essential for muscle maintenance.
Figures
References
-
- Bamburg J.R. Proteins of the ADF/cofilin family: essential regulators of actin dynamics. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 1999;15:185–230. - PubMed
-
- Agrawal P.B., Greenleaf R.S., Tomczak K.K., Lehtokari V.L., Wallgren-Pettersson C., Wallefeld W., Laing N.G., Darras B.T., Maciver S.K., Dormitzer P.R., et al. Nemaline myopathy with minicores caused by mutation of the CFL2 gene encoding the skeletal muscle actin-binding protein, cofilin-2. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007;80:162–167. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Thirion C., Stucka R., Mendel B., Gruhler A., Jaksch M., Nowak K.J., Binz N., Laing N.G., Lochmuller H. Characterization of human muscle type cofilin (CFL2) in normal and regenerating muscle. Eur. J. Biochem. 2001;268:3473–3482. - PubMed
-
- Mohri K., Takano-Ohmuro H., Nakashima H., Hayakawa K., Endo T., Hanaoka K., Obinata T. Expression of cofilin isoforms during development of mouse striated muscles. J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 2000;21:49–57. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

