Meta-analysis of untargeted metabolomic data from multiple profiling experiments
- PMID: 22343432
- PMCID: PMC3683249
- DOI: 10.1038/nprot.2011.454
Meta-analysis of untargeted metabolomic data from multiple profiling experiments
Abstract
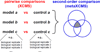
metaXCMS is a software program for the analysis of liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry-based untargeted metabolomic data. It is designed to identify the differences between metabolic profiles across multiple sample groups (e.g., 'healthy' versus 'active disease' versus 'inactive disease'). Although performing pairwise comparisons alone can provide physiologically relevant data, these experiments often result in hundreds of differences, and comparison with additional biologically meaningful sample groups can allow for substantial data reduction. By performing second-order (meta-) analysis, metaXCMS facilitates the prioritization of interesting metabolite features from large untargeted metabolomic data sets before the rate-limiting step of structural identification. Here we provide a detailed step-by-step protocol for going from raw mass spectrometry data to metaXCMS results, visualized as Venn diagrams and exported Microsoft Excel spreadsheets. There is no upper limit to the number of sample groups or individual samples that can be compared with the software, and data from most commercial mass spectrometers are supported. The speed of the analysis depends on computational resources and data volume, but will generally be less than 1 d for most users. metaXCMS is freely available at http://metlin.scripps.edu/metaxcms/.
Figures





References
-
- Baker M. Metabolomics: from small molecules to big ideas. Nat Meth. 2011;8:117–121.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

