A high-affinity, dimeric inhibitor of PSD-95 bivalently interacts with PDZ1-2 and protects against ischemic brain damage
- PMID: 22343531
- PMCID: PMC3295328
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1113761109
A high-affinity, dimeric inhibitor of PSD-95 bivalently interacts with PDZ1-2 and protects against ischemic brain damage
Abstract
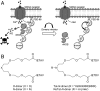
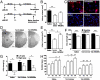
Inhibition of the ternary protein complex of the synaptic scaffolding protein postsynaptic density protein-95 (PSD-95), neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS), and the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor is a potential strategy for treating ischemic brain damage, but high-affinity inhibitors are lacking. Here we report the design and synthesis of a novel dimeric inhibitor, Tat-NPEG4(IETDV)(2) (Tat-N-dimer), which binds the tandem PDZ1-2 domain of PSD-95 with an unprecedented high affinity of 4.6 nM, and displays extensive protease-resistance as evaluated in vitro by stability-measurements in human blood plasma. X-ray crystallography, NMR, and small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) deduced a true bivalent interaction between dimeric inhibitor and PDZ1-2, and also provided a dynamic model of the conformational changes of PDZ1-2 induced by the dimeric inhibitor. A single intravenous injection of Tat-N-dimer (3 nmol/g) to mice subjected to focal cerebral ischemia reduces infarct volume with 40% and restores motor functions. Thus, Tat-N-dimer is a highly efficacious neuroprotective agent with therapeutic potential in stroke.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Comment in
-
Stroke: Can PSD95 inhibitors widen the therapeutic window?Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2012 Mar 30;11(4):272. doi: 10.1038/nrd3716. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2012. PMID: 22460120 No abstract available.
References
-
- Blazer LL, Neubig RR. Small molecule protein-protein interaction inhibitors as CNS therapeutic agents: Current progress and future hurdles. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2009;34:126–141. - PubMed
-
- Dev KK. Making protein interactions druggable:Targeting PDZ domains. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2004;3:1047–1056. - PubMed
-
- Christopherson KS, Hillier BJ, Lim WA, Bredt DS. PSD-95 assembles a ternary complex with the N-methyl-d-aspartic acid receptor and a bivalent neuronal NO synthase PDZ domain. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:27467–27473. - PubMed
-
- Sattler R, et al. Specific coupling of NMDA receptor activation to nitric oxide neurotoxicity by PSD-95 protein. Science. 1999;284:1845–1848. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

