The MEK1/2 inhibitor, selumetinib (AZD6244; ARRY-142886), enhances anti-tumour efficacy when combined with conventional chemotherapeutic agents in human tumour xenograft models
- PMID: 22343622
- PMCID: PMC3305954
- DOI: 10.1038/bjc.2012.8
The MEK1/2 inhibitor, selumetinib (AZD6244; ARRY-142886), enhances anti-tumour efficacy when combined with conventional chemotherapeutic agents in human tumour xenograft models
Abstract
Background: The Ras/RAF/MEK/ERK pathway is frequently deregulated in cancer and a number of inhibitors that target this pathway are currently in clinical development. It is likely that clinical testing of these agents will be in combination with standard therapies to harness the apoptotic potential of both the agents. To support this strategy, it has been widely observed that a number of chemotherapeutics stimulate the activation of several intracellular signalling cascades including Ras/RAF/MEK/ERK. The MEK1/2 inhibitor selumetinib has been shown to have anti-tumour activity and induce apoptotic cell death as a monotherapy.
Methods: The aim of this study was to identify agents, which would be likely to offer clinical benefit when combined with selumetinib. Here, we used human tumour xenograft models and assessed the effects combining standard chemotherapeutic agents with selumetinib on tumour growth. In addition, we analysed tumour tissue to determine the mechanistic effects of these combinations.
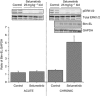
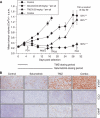
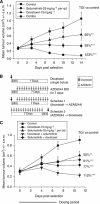
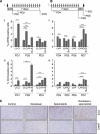
Results: Combining selumetinib with the DNA-alkylating agent, temozolomide (TMZ), resulted in enhanced tumour growth inhibition compared with monotherapies. Biomarker studies highlighted an increase in γH2A.X suggesting that selumetinib is able to enhance the DNA damage induced by TMZ alone. In several models we observed that continuous exposure to selumetinib in combination with docetaxel results in tumour regression. Scheduling of docetaxel before selumetinib was more beneficial than when selumetinib was dosed before docetaxel and demonstrated a pro-apoptotic phenotype. Similar results were seen when selumetinib was combined with the Aurora B inhibitor barasertib.
Conclusion: The data presented suggests that MEK inhibition in combination with several standard chemotherapeutics or an Aurora B kinase inhibitor is a promising clinical strategy.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors are/were employees or receiving post-doctoral funding from AstraZeneca pharmaceuticals at the time this work was performed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MEK1/2 inhibitor selumetinib (AZD6244) inhibits growth of ovarian clear cell carcinoma in a PEA-15-dependent manner in a mouse xenograft model.Mol Cancer Ther. 2012 Feb;11(2):360-9. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-11-0400. Epub 2011 Dec 5. Mol Cancer Ther. 2012. PMID: 22144664 Free PMC article.
-
Acute tumour response to the MEK1/2 inhibitor selumetinib (AZD6244, ARRY-142886) evaluated by non-invasive diffusion-weighted MRI.Br J Cancer. 2013 Sep 17;109(6):1562-9. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2013.456. Epub 2013 Aug 13. Br J Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23942066 Free PMC article.
-
Combined MEK and VEGFR inhibition in orthotopic human lung cancer models results in enhanced inhibition of tumor angiogenesis, growth, and metastasis.Clin Cancer Res. 2012 Mar 15;18(6):1641-54. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-2324. Epub 2012 Jan 24. Clin Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22275507 Free PMC article.
-
Selumetinib in the treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer.Future Oncol. 2016 Nov;12(22):2545-2560. doi: 10.2217/fon-2016-0132. Epub 2016 Jul 28. Future Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27467210 Review.
-
Treating non-small cell lung cancer with selumetinib: an up-to-date drug evaluation.Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2020 Nov;21(16):1943-1953. doi: 10.1080/14656566.2020.1798930. Epub 2020 Sep 3. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 32880495 Review.
Cited by
-
Glioblastoma-Derived Exosomes as Nanopharmaceutics for Improved Glioma Treatment.Pharmaceutics. 2022 May 6;14(5):1002. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14051002. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 35631588 Free PMC article.
-
mTOR Signaling in Protein Translation Regulation: Implications in Cancer Genesis and Therapeutic Interventions.Mol Biol Int. 2014;2014:686984. doi: 10.1155/2014/686984. Epub 2014 Nov 20. Mol Biol Int. 2014. PMID: 25505994 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Co-dependency between KRAS addiction and ARHGEF2 promotes an adaptive escape from MAPK pathway inhibition.Small GTPases. 2019 Nov;10(6):441-448. doi: 10.1080/21541248.2017.1337545. Epub 2017 Jul 11. Small GTPases. 2019. PMID: 28656876 Free PMC article.
-
MEK1/2 inhibition suppresses tamoxifen toxicity on CNS glial progenitor cells.J Neurosci. 2013 Sep 18;33(38):15069-74. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2729-13.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 24048837 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of immunoglobulin transcription factor 2 and resistance to MEK inhibitor in melanoma cells.Oncotarget. 2017 Jun 20;8(25):41387-41400. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.17866. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28574827 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Banerji U, Camidge DR, Verheul HM, Agarwal R, Sarker D, Kaye SB, Desar IM, Timmer-Bonte JN, Eckhardt SG, Lewis KD, Brown KH, Cantarini MV, Morris C, George SM, Smith PD, van Herpen CM (2010) The first-in-human study of the hydrogen sulfate (Hyd-sulfate) capsule of the MEK1/2 inhibitor AZD6244 (ARRY-142886): a phase I open-label multicenter trial in patients with advanced cancer. Clin Cancer Res 16: 1613–1623 - PubMed
-
- Bhatt KV, Spofford LS, Aram G, McMullen M, Pumiglia K, Aplin AE (2005) Adhesion control of cyclin D1 and p27Kip1 levels is deregulated in melanoma cells through BRAF-MEK-ERK signaling. Oncogene 24: 3459–3471 - PubMed
-
- Biswas SC, Greene LA (2002) Nerve growth factor (NGF) down-regulates the Bcl-2 homology 3 (BH3) domain-only protein Bim and suppresses its proapoptotic activity by phosphorylation. J Biol Chem 277: 49511–49516 - PubMed
-
- Cui Y, Guadagno TM (2008) B-Raf(V600E) signaling deregulates the mitotic spindle checkpoint through stabilizing Mps1 levels in melanoma cells. Oncogene 27: 3122–3133 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

