Cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers and proximity to diagnosis in preclinical familial Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 22343824
- PMCID: PMC3696356
- DOI: 10.1159/000335729
Cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers and proximity to diagnosis in preclinical familial Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
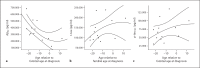
Background/aims: Biological markers of utility in tracking Alzheimer's disease (AD) during the presymptomatic prodromal phase are important for prevention studies. Changes in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) levels of 42-amino-acid β-amyloid (Aβ(42)), total tau protein (t-tau) and phosphorylated tau at residue 181 (p-tau(181)) during this state are incompletely characterized.
Methods: We measured CSF markers in 13 carriers of familial AD (FAD) mutations that are fully penetrant for causing AD (PSEN1 and APP) and in 5 non-mutation-carrying family members.
Results: Even among the entirely presymptomatic mutation carriers (n = 9), Aβ(42) was diminished (388.7 vs. 618.4 pg/ml, p = 0.004), and t-tau (138.5 vs. 50.5 pg/ml, p = 0.002) and p-tau(181) (71.7 vs. 24.6 pg/ml, p = 0.003) were elevated. There was a negative correlation between Aβ(42) levels and age relative to the family-specific age of dementia diagnosis.
Conclusions: Our data are consistent with a decline in CSF Aβ(42) levels occurring at least 20 years prior to clinical dementia in FAD.
Copyright © 2012 S. Karger AG, Basel.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Preclinical cerebrospinal fluid and volumetric magnetic resonance imaging biomarkers in Swedish familial Alzheimer's disease.J Alzheimers Dis. 2015;43(4):1393-402. doi: 10.3233/JAD-140339. J Alzheimers Dis. 2015. PMID: 25182737
-
PSEN1 mutation carriers present lower cerebrospinal fluid amyoid-β42 levels than sporadic early-onset Alzheimer's disease patients but no differences in neuronal injury biomarkers.J Alzheimers Dis. 2012;30(3):605-16. doi: 10.3233/JAD-2012-111949. J Alzheimers Dis. 2012. PMID: 22426017
-
The Effects of Gene Mutations on Default Mode Network in Familial Alzheimer's Disease.J Alzheimers Dis. 2017;56(1):327-334. doi: 10.3233/JAD-160730. J Alzheimers Dis. 2017. PMID: 27911308
-
Simultaneous analysis of cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers using microsphere-based xMAP multiplex technology for early detection of Alzheimer's disease.Methods. 2012 Apr;56(4):484-93. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2012.03.023. Epub 2012 Apr 6. Methods. 2012. PMID: 22503777 Review.
-
Clinical utility and analytical challenges in measurement of cerebrospinal fluid amyloid-β(1-42) and τ proteins as Alzheimer disease biomarkers.Clin Chem. 2013 Jun;59(6):903-16. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2013.202937. Epub 2013 Mar 21. Clin Chem. 2013. PMID: 23519967 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Conformation-dependent oligomers in cerebrospinal fluid of presymptomatic familial Alzheimer's disease mutation carriers.Dement Geriatr Cogn Dis Extra. 2012 Jan;2(1):652-7. doi: 10.1159/000345771. Epub 2012 Dec 15. Dement Geriatr Cogn Dis Extra. 2012. PMID: 23341831 Free PMC article.
-
PSEN1 c.1292C<A Variant and Early-Onset Alzheimer's Disease: A Scoping Review.Front Aging Neurosci. 2022 Jul 22;14:860529. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.860529. eCollection 2022. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35959289 Free PMC article.
-
A cross-sectional study on cerebrospinal fluid biomarker levels in cognitively normal elderly subjects with or without a family history of Alzheimer's disease.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2013 Jan;19(1):38-42. doi: 10.1111/cns.12028. Epub 2012 Nov 22. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2013. PMID: 23171371 Free PMC article.
-
Autosomal Dominant Alzheimer Disease: A Unique Resource to Study CSF Biomarker Changes in Preclinical AD.Front Neurol. 2015 Jun 29;6:142. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2015.00142. eCollection 2015. Front Neurol. 2015. PMID: 26175713 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alzheimer's disease: Unique markers for diagnosis & new treatment modalities.Indian J Med Res. 2015 Oct;142(4):369-82. doi: 10.4103/0971-5916.169193. Indian J Med Res. 2015. PMID: 26609028 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Thies W, Bleiler L. Alzheimer's disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement. 2011;7:208–244. - PubMed
-
- Motter R, Vigo-Pelfrey C, Kholodenko D, et al. Reduction of beta-amyloid peptide42 in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with Alzheimer's disease. Ann Neurol. 1995;38:643–648. - PubMed
-
- Zetterberg H, Hietala MA, Jonsson M, et al. Neurochemical aftermath of amateur boxing. Arch Neurol. 2006;63:1277–1280. - PubMed
-
- Hesse C, Rosengren L, Andreasen N, et al. Transient increase in total tau but not phospho-tau in human cerebrospinal fluid after acute stroke. Neurosci Lett. 2001;297:187–190. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical