Estimating the proportion of variation in susceptibility to schizophrenia captured by common SNPs
- PMID: 22344220
- PMCID: PMC3327879
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.1108
Estimating the proportion of variation in susceptibility to schizophrenia captured by common SNPs
Abstract
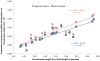
Schizophrenia is a complex disorder caused by both genetic and environmental factors. Using 9,087 affected individuals, 12,171 controls and 915,354 imputed SNPs from the Schizophrenia Psychiatric Genome-Wide Association Study (GWAS) Consortium (PGC-SCZ), we estimate that 23% (s.e. = 1%) of variation in liability to schizophrenia is captured by SNPs. We show that a substantial proportion of this variation must be the result of common causal variants, that the variance explained by each chromosome is linearly related to its length (r = 0.89, P = 2.6 × 10(-8)), that the genetic basis of schizophrenia is the same in males and females, and that a disproportionate proportion of variation is attributable to a set of 2,725 genes expressed in the central nervous system (CNS; P = 7.6 × 10(-8)). These results are consistent with a polygenic genetic architecture and imply more individual SNP associations will be detected for this disease as sample size increases.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures


References
-
- Sullivan PF, Kendler KS, Neale MC. Schizophrenia as a complex trait -Evidence from a meta-analysis of twin studies. Archives of General Psychiatry. 2003;60:1187–1192. - PubMed
-
- Cardno AG, Gottesman II. Twin studies of schizophrenia: from bow-and-arrow concordances to star wars Mx and functional genomics. Am J Med Genet. 2000;97:12–17. - PubMed
-
- McClellan JM, Susser E, King MC. Schizophrenia: a common disease caused by multiple rare alleles. British Journal of Psychiatry. 2007;190:194–199. - PubMed
-
- Craddock N, O’Donovan MC, Owen MJ. Phenotypic and genetic complexity of psychosis -Invited commentary on … Schizophrenia: a common disease caused by multiple rare alleles. British Journal of Psychiatry. 2007;190:200–203. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- U01 MH085520/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH085812/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH078075/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH058693/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K01 MH085812/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P30 MH074543/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH067257/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH079470/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059587/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH085548/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059586/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P50 MH066392/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- N01 MH090001/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH074027/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH061675/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K23 MH001760/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR018535/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH079800/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH061884/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH084098/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH046276/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH077139/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH079469/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH071681/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH060870/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH081800/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059571/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059565/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH046289/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH080403/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH052618/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059566/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059588/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH046318/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U54 RR020278/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH085542/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH060879/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

