Common variants at CDKAL1 and KLF9 are associated with body mass index in east Asian populations
- PMID: 22344221
- PMCID: PMC3838874
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.1086
Common variants at CDKAL1 and KLF9 are associated with body mass index in east Asian populations
Abstract
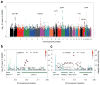
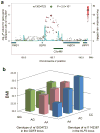
Obesity is a disorder with a complex genetic etiology, and its epidemic is a worldwide problem. Although multiple genetic loci associated with body mass index, the most common measure of obesity, have been identified in European populations, few studies have focused on Asian populations. Here we report a genome-wide association study and replication studies with 62,245 east Asian subjects, which identified two new body mass index-associated loci in the CDKAL1 locus at 6p22 (rs2206734, P = 1.4 × 10(-11)) and the KLF9 locus at 9q21 (rs11142387, P = 1.3 × 10(-9)), as well as several previously reported loci (the SEC16B, BDNF, FTO, MC4R and GIPR loci, P < 5.0 × 10(-8)). We subsequently performed gene-gene interaction analyses and identified an interaction (P = 2.0 × 10(-8)) between a SNP in the KLF9 locus (rs11142387) and one in the MSTN (also known as GDF8) locus at 2q32 (rs13034723). These findings should provide useful insights into the etiology of obesity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
References
-
- Kopelman PG. Obesity as a medical problem. Nature. 2000;404:635–643. - PubMed
-
- Maes HH, Neale MC, Eaves LJ. Genetic and environmental factors in relative body weight and human adiposity. Behav Genet. 1997;27:325–351. - PubMed
-
- Chambers JC, et al. Common genetic variation near MC4R is associated with waist circumference and insulin resistance. Nat Genet. 2008;40:716–718. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

