Employing a recombinant strain of Advenella mimigardefordensis for biotechnical production of Homopolythioesters from 3,3'-dithiodipropionic acid
- PMID: 22344658
- PMCID: PMC3346455
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.00007-12
Employing a recombinant strain of Advenella mimigardefordensis for biotechnical production of Homopolythioesters from 3,3'-dithiodipropionic acid
Abstract
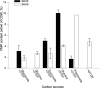
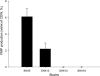
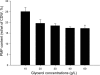
Advenella mimigardefordensis strain DPN7(T) was genetically modified to produce poly(3-mercaptopropionic acid) (PMP) homopolymer by exploiting the recently unraveled process of 3,3'-dithiodipropionic acid (DTDP) catabolism. Production was achieved by systematically engineering the metabolism of this strain as follows: (i) deletion of its inherent 3MP dioxygenase-encoding gene (mdo), (ii) introduction of the buk-ptb operon (genes encoding the butyrate kinase, Buk, and the phosphotransbutyrylase, Ptb, from Clostridium acetobutylicum), and (iii) overexpression of its own polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase (phaC(Am)). These measures yielded the potent PMP production strain A. mimigardefordensis strain SHX22. The deletion of mdo was required for adequate synthesis of PMP due to the resulting accumulation of 3MP during utilization of DTDP. Overexpression of the plasmid-borne buk-ptb operon caused a severe growth repression. This effect was overcome by inserting this operon into the genome. Polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) synthases from different origins were compared. The native PHA synthase of A. mimigardefordensis (phaC(Am)) was obviously the best choice to establish homopolythioester production in this strain. In addition, the cultivation conditions, including an appropriate provision of the carbon source, were further optimized to enhance PMP production. The engineered strain accumulated PMP up to approximately 25% (wt/wt) of the cell dry weight when cultivated in mineral salts medium containing glycerol as the carbon source in addition to DTDP as the sulfur-providing precursor. According to our knowledge, this is the first report of PMP homopolymer production by a metabolically engineered bacterium using DTDP, which is nontoxic, as the precursor substrate.
Figures





References
-
- Bruland N, Wübbeler JH, Steinbüchel A. 2009. 3-Mercaptopropionate dioxygenase, a cysteine dioxygenase homologue, catalyzes the initial step of 3-mercaptopropionate catabolism in the 3,3-thiodipropionic acid-degrading bacterium Variovorax paradoxus. J. Biol. Chem. 284:660–672 - PubMed
-
- Coenye T, et al. 2005. Advenella incenata gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel member of the Alcaligenaceae, isolated from various clinical samples. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 55:251–256 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

