Student Award for Outstanding Research Winner in the Ph.D. Category for the 9th World Biomaterials Congress, Chengdu, China, June 1-5, 2012: The interplay of bone-like extracellular matrix and TNF-α signaling on in vitro osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells
- PMID: 22345065
- PMCID: PMC3312972
- DOI: 10.1002/jbm.a.34058
Student Award for Outstanding Research Winner in the Ph.D. Category for the 9th World Biomaterials Congress, Chengdu, China, June 1-5, 2012: The interplay of bone-like extracellular matrix and TNF-α signaling on in vitro osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells
Abstract
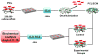
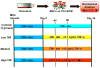
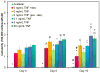
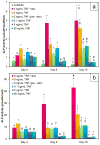
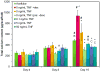
As an initial step in the development of a bone tissue engineering strategy to rationally control inflammation, we investigated the interplay of bone-like extracellular matrix (ECM) and varying doses of the inflammatory cytokine tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) on osteogenically differentiating mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) cultured in vitro on 3D poly(ε-caprolactone) (PCL) microfiber scaffolds containing pregenerated bone-like ECM. To generate the ECM, PCL scaffolds were seeded with MSCs and cultured in medium containing the typically required osteogenic supplement dexamethasone. However, since dexamethasone antagonizes TNF-α, the interplay of ECM and TNF-α was investigated by culturing naïve MSCs on the decellularized scaffolds in the absence of dexamethasone. MSCs cultured on ECM-coated scaffolds continued to deposit mineralized matrix, a late stage marker of osteogenic differentiation. Mineralized matrix deposition was not adversely affected by exposure to TNF-α for 4-8 days, but was significantly reduced after continuous exposure to TNF-α over 16 days, which simulates the in vivo response, where brief TNF-α signaling stimulates bone regeneration, while prolonged exposure has damaging effects. This underscores the exciting potential of PCL/ECM constructs as a more clinically realistic in vitro culture model to facilitate the design of new bone tissue engineering strategies that rationally control inflammation to promote regeneration.
Copyright © 2012 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Effect of temporally patterned TNF-α delivery on in vitro osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells cultured on biodegradable polymer scaffolds.J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2013;24(15):1794-813. doi: 10.1080/09205063.2013.803455. Epub 2013 Jun 8. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2013. PMID: 23746285 Free PMC article.
-
Osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells on pregenerated extracellular matrix scaffolds in the absence of osteogenic cell culture supplements.Tissue Eng Part A. 2010 Feb;16(2):431-40. doi: 10.1089/ten.TEA.2009.0583. Tissue Eng Part A. 2010. PMID: 19863274 Free PMC article.
-
Dose effect of tumor necrosis factor-alpha on in vitro osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells on biodegradable polymeric microfiber scaffolds.Biomaterials. 2010 Mar;31(7):1666-75. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2009.11.058. Epub 2009 Dec 5. Biomaterials. 2010. PMID: 19963268 Free PMC article.
-
Winner of the 2013 Young Investigator Award for the Society for Biomaterials annual meeting and exposition, April 10-13, 2013, Boston, Massachusetts. Osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells on demineralized and devitalized biodegradable polymer and extracellular matrix hybrid constructs.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2013 May;101(5):1225-36. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.34610. Epub 2013 Mar 16. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2013. PMID: 23505119 Free PMC article.
-
Self-assembled composite matrix in a hierarchical 3-D scaffold for bone tissue engineering.Acta Biomater. 2011 May;7(5):2244-55. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2010.12.031. Epub 2010 Dec 31. Acta Biomater. 2011. PMID: 21195810
Cited by
-
The Host Response in Tissue Engineering: Crosstalk Between Immune cells and Cell-laden Scaffolds.Curr Opin Biomed Eng. 2018 Jun;6:58-65. doi: 10.1016/j.cobme.2018.03.006. Epub 2018 Mar 31. Curr Opin Biomed Eng. 2018. PMID: 30374467 Free PMC article.
-
Revealing cytokine-induced changes in the extracellular matrix with secondary ion mass spectrometry.Acta Biomater. 2015 Mar;14:70-83. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2014.12.005. Epub 2014 Dec 15. Acta Biomater. 2015. PMID: 25523877 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of temporally patterned TNF-α delivery on in vitro osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells cultured on biodegradable polymer scaffolds.J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2013;24(15):1794-813. doi: 10.1080/09205063.2013.803455. Epub 2013 Jun 8. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2013. PMID: 23746285 Free PMC article.
-
Sustained delivery of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 from perlecan domain I - functionalized electrospun poly (ε-caprolactone) scaffolds for bone regeneration.J Exp Orthop. 2016 Dec;3(1):25. doi: 10.1186/s40634-016-0057-1. Epub 2016 Oct 6. J Exp Orthop. 2016. PMID: 27714703 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kolar P, Schmidt-Bleek K, Schell H, Gaber T, Toben D, Schmidmaier G, Perka C, Buttgereit F, Duda GN. The early fracture hematoma and its potential role in fracture healing. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2010;16(4):427–434. - PubMed
-
- Pape H-C, Marcucio R, Humphrey C, Colnot C, Knobe M, Harvey EJ. Trauma-induced inflammation and fracture healing. J Orthop Trauma. 2010;24(9):522–525. - PubMed
-
- Rundle CH, Wang H, Yu H, Chadwick RB, Davis EI, Wegedal JE, Lau K-HW, Mohan S, Ryaby JT, Baylink DJ. Microarray analysis of gene expression during the inflammation and endochondral bone formation stages of rat femur fracture repair. Bone. 2006;38:521–529. - PubMed
-
- Kitaori T, Ito H, Schwarz EM, Tsutsumi R, Yoshitomi H, Oishi S, Nakano M, Fujii N, Nagasawa T, Nakamura T. Stromal cell–derived factor 1/CXCR4 signaling is critical for the recruitment of mesenchymal stem cells to the fracture site during skeletal repair in a mouse model. Arthritis Rheum. 2009;60(3):813–823. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

