Receptor-binding profiles of H7 subtype influenza viruses in different host species
- PMID: 22345462
- PMCID: PMC3318648
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.06959-11
Receptor-binding profiles of H7 subtype influenza viruses in different host species
Abstract
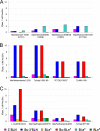
Influenza viruses of gallinaceous poultry and wild aquatic birds usually have distinguishable receptor-binding properties. Here we used a panel of synthetic sialylglycopolymers and solid-phase receptor-binding assays to characterize receptor-binding profiles of about 70 H7 influenza viruses isolated from aquatic birds, land-based poultry, and horses in Eurasia and America. Unlike typical duck influenza viruses with non-H7 hemagglutinin (HA), all avian H7 influenza viruses, irrespective of the host species, displayed a poultry-virus-like binding specificity, i.e., preferential binding to sulfated oligosaccharides Neu5Acα2-3Galβ1-4(6-O-HSO(3))GlcNAc and Neu5Acα2-3Galβ1-4(Fucα1-3)(6-O-HSO(3))GlcNAc. This phenotype correlated with the unique amino acid sequence of the amino acid 185 to 189 loop of H7 HA and seemed to be dependent on ionic interactions between the sulfate group of the receptor and Lys193 and on the lack of sterical clashes between the fucose residue and Gln222. Many North American and Eurasian H7 influenza viruses displayed weak but detectable binding to the human-type receptor moiety Neu5Acα2-6Galβ1-4GlcNAc, highlighting the potential of H7 influenza viruses for avian-to-human transmission. Equine H7 influenza viruses differed from other viruses by preferential binding to the N-glycolyl form of sialic acid. Our data suggest that the receptor-binding site of contemporary H7 influenza viruses in aquatic and terrestrial birds was formed after the introduction of their common precursor from ducks to a new host, presumably, gallinaceous poultry. The uniformity of the receptor-binding profile of H7 influenza viruses in various wild and domestic birds indicates that there is no strong receptor-mediated host range restriction in birds on viruses with this HA subtype. This notion agrees with repeated interspecies transmission of H7 influenza viruses from aquatic birds to poultry.
Figures

References
-
- Baigent SJ, McCauley JW. 2003. Influenza type A in humans, mammals and birds: determinants of virus virulence, host-range and interspecies transmission. Bioessays 25:657–671 - PubMed
-
- Banks J, et al. 2001. Changes in the haemagglutinin and the neuraminidase genes prior to the emergence of highly pathogenic H7N1 avian influenza viruses in Italy. Arch. Virol. 146:963–973 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

