PR-Set7 and H4K20me1: at the crossroads of genome integrity, cell cycle, chromosome condensation, and transcription
- PMID: 22345514
- PMCID: PMC3289880
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.177444.111
PR-Set7 and H4K20me1: at the crossroads of genome integrity, cell cycle, chromosome condensation, and transcription
Abstract
Histone post-translational modifications impact many aspects of chromatin and nuclear function. Histone H4 Lys 20 methylation (H4K20me) has been implicated in regulating diverse processes ranging from the DNA damage response, mitotic condensation, and DNA replication to gene regulation. PR-Set7/Set8/KMT5a is the sole enzyme that catalyzes monomethylation of H4K20 (H4K20me1). It is required for maintenance of all levels of H4K20me, and, importantly, loss of PR-Set7 is catastrophic for the earliest stages of mouse embryonic development. These findings have placed PR-Set7, H4K20me, and proteins that recognize this modification as central nodes of many important pathways. In this review, we discuss the mechanisms required for regulation of PR-Set7 and H4K20me1 levels and attempt to unravel the many functions attributed to these proteins.
Figures
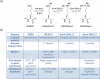

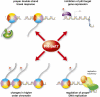
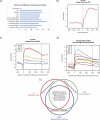
References
-
- Arias EE, Walter JC 2006. PCNA functions as a molecular platform to trigger Cdt1 destruction and prevent re-replication. Nat Cell Biol 8: 84–90 - PubMed
-
- Arias EE, Walter JC 2007. Strength in numbers: Preventing rereplication via multiple mechanisms in eukaryotic cells. Genes & Dev 21: 497–518 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
