Site-specific DNA-antibody conjugates for specific and sensitive immuno-PCR
- PMID: 22345566
- PMCID: PMC3309776
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1120682109
Site-specific DNA-antibody conjugates for specific and sensitive immuno-PCR
Abstract
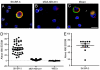
Antibody conjugates are widely used as diagnostics and imaging reagents. However, many such conjugates suffer losses in sensitivity and specificity due to nonspecific labeling techniques. We have developed methodology to site-specifically conjugate oligonucleotides to antibodies containing a genetically encoded unnatural amino acid with orthogonal chemical reactivity. These oligobody molecules were used in immuno-PCR assays to detect Her2(+) cells with greater sensitivity and specificity than nonspecifically coupled fragments, and can detect extremely rare Her2(+) cells in a complex cellular environment. Such designed antibody-oligonucleotide conjugates should provide sensitive and specific reagents for diagnostics, as well as enable other unique applications based on oligobody building blocks.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Nam JM, Thaxton CS, Mirkin CA. Nanoparticle-based bio-bar codes for the ultrasensitive detection of proteins. Science. 2003;301:1884–1886. - PubMed
-
- Sano T, Smith CL, Cantor CR. Immuno-PCR: Very sensitive antigen detection by means of specific antibody-DNA conjugates. Science. 1992;258:120–122. - PubMed
-
- Niemeyer CM, Adler M, Wacker R. Detecting antigens by quantitative immuno-PCR. Nat Protoc. 2007;2:1918–1930. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

