Neurological disorders and barriers for neurological rehabilitation in rural areas in Uttar Pradesh: A cross-sectional study
- PMID: 22346183
- PMCID: PMC3271604
- DOI: 10.4103/0976-3147.91923
Neurological disorders and barriers for neurological rehabilitation in rural areas in Uttar Pradesh: A cross-sectional study
Abstract
Background: In India, the majority of individuals with neurological disorders are rural based and cannot even afford the cost of rehabilitation. At the same time, we do not have barrier free environment in India.
Aim: This study attempts to find out the neurological disorders and barriers for neurological rehabilitation in rural areas in Uttar Pradesh, India.
Setting: Rural areas in Uttar Pradesh, India.
Design: It is a cross-sectional study.
Materials and methods: The study was done by means of an interview method using a questionnaire. The rural areas in Uttar Pradesh were visited personally and a data from 201 individuals was collected.
Statistical analysis used: Data analysis was done by using descriptive statistics.
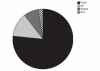
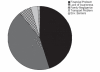
Results: Out of 201 individuals, 76.6% (n=154) individuals were with polio, 12.9% (n=26) were with cerebral palsy, 7.9% (n=16) were with stroke and 2.4% (n=5) were with spinal cord injury. Reasons for not taking the treatment/discontinuation of treatment were financial problem (44%), lack of awareness (43%), family negligence (6%), transportation problem (3.5%) and other environmental barriers (1%).
Conclusion: In our study, we found polio to be the most prevalent disorder followed by Cerebral Palsy, Stroke and Spinal Cord Injury. Financial problem was the major barrier for neurological rehabilitation followed by lack of awareness, family negligence and transportation problem.
Keywords: Disability; environmental barriers; neurological disorders; poverty; rehabilitation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
What needs to be done for polio eradication in India?Vaccine. 2007 Aug 29;25(35):6431-6. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2007.05.059. Epub 2007 Jun 15. Vaccine. 2007. PMID: 17646037
-
Analysis of birth intervals in India's Uttar Pradesh and Kerala States.J Biosoc Sci. 1993 Apr;25(2):143-53. doi: 10.1017/s0021932000020459. J Biosoc Sci. 1993. PMID: 8478365
-
Outcomes of polio eradication activities in Uttar Pradesh, India: the Social Mobilization Network (SM Net) and Core Group Polio Project (CGPP).BMC Infect Dis. 2011 May 10;11:117. doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-11-117. BMC Infect Dis. 2011. PMID: 21569256 Free PMC article.
-
Support for children identified with acute flaccid paralysis under the global polio eradication programme in Uttar Pradesh, India: a qualitative study.BMC Public Health. 2012 Mar 22;12:229. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-12-229. BMC Public Health. 2012. PMID: 22439606 Free PMC article.
-
Why polio has not been eradicated in India despite many remedial interventions?Vaccine. 2009 Jun 8;27(28):3700-3. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2009.03.078. Epub 2009 Apr 16. Vaccine. 2009. PMID: 19464552 Review.
Cited by
-
Importance of preliminary epidemiology studies in rural areas of developing countries.J Neurosci Rural Pract. 2012 Jan;3(1):2-3. doi: 10.4103/0976-3147.91920. J Neurosci Rural Pract. 2012. PMID: 22346180 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Commentary.J Neurosci Rural Pract. 2012 Jan;3(1):16. J Neurosci Rural Pract. 2012. PMID: 22346184 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Factors Influencing Utilization of Physiotherapy Service among Children with Cerebral Palsy in Jalandhar District of Punjab.J Neurosci Rural Pract. 2017 Apr-Jun;8(2):209-215. doi: 10.4103/0976-3147.203852. J Neurosci Rural Pract. 2017. PMID: 28479794 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of a training program for community health officers on neurological disorders: insights from the Karnataka brain health initiative.BMC Health Serv Res. 2025 Jul 3;25(1):924. doi: 10.1186/s12913-025-12549-4. BMC Health Serv Res. 2025. PMID: 40611095 Free PMC article.
-
The burden of neurological disorders across the states of India: the Global Burden of Disease Study 1990-2019.Lancet Glob Health. 2021 Aug;9(8):e1129-e1144. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(21)00164-9. Epub 2021 Jul 14. Lancet Glob Health. 2021. PMID: 34273302 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Neurological Disorder. [Last accessed on 2011 Mar 18]. Available from: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Neurological_disorder .
-
- Sandberg MA, Bush SS, Martin T. Beyond diagnosis: Understanding the healthcare challenges of injured veterans through the application of the International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health (ICF) Clin Neuropsychol. 2009;23:1416–32. - PubMed
-
- Chandre V, Pandav CS. The importance of non-communicable disease in developing countries (editorial) Ind J Com Med. 1987;12:178–80.
-
- Gourie-Devi M. Can India offord neuroepidemiology. Neurol India. 1987;35:125–7.
-
- Sekaran P, Vijayakumari F, Hariharan R, Zachariah K, Joseph SE, Kumar RK. Community reintegration of spinal cord-injured patients in rural south India. Spinal Cord. 2010;48:628–32. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources