Carotid intima-media thickness and apolipoproteins in patients of ischemic stroke in a rural hospital setting in central India: A cross-sectional study
- PMID: 22346186
- PMCID: PMC3271608
- DOI: 10.4103/0976-3147.91926
Carotid intima-media thickness and apolipoproteins in patients of ischemic stroke in a rural hospital setting in central India: A cross-sectional study
Abstract
Context: Carotid intima-media thickness (CIMT) and apolipoproteins have been found as a risk factor for ischemic stroke
Objective: The objective was to study the carotid intima-media thickness, apolipoproteins, and their relation in patients of ischemic stroke in central rural India.
Settings and design: A cross-sectional study was performed in a rural hospital in central India.
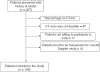
Materials and methods: In all patients of ischemic stroke proven by computerized tomography (CT), CIMT, apolipoprotein A-I (ApoA-I), and apolipoprotein B(ApoB) were measured.
Statistical analysis used: We used Student's t-test to compare means, a chi-square test to compare proportions, and a Mann-Whitney test to compare medians. A P value <0.05 was considered significant.
Results: The mean age of our study population (N=106) was 61 years. The mean CIMT was 0.83 mm ranging from a minimum of 0.45 mm to a maximum of 1.096 mm. Mean CIMT was significantly higher than expected 0.67 values, which was calculated according to the age of the study population. The association of decreased ApoA-I < 100 mg/dl and increased ApoB > 90 mg/dl with CIMT > 0.7 mm was statistically significant with P<0.001.
Conclusions: The CIMT in computerized tomography-proven ischemic stroke was significantly higher than expected for the age of the study population. The relation of decreased ApoA-I and increased ApoB with CIMT > 0.7 mm was also statistically significant.
Keywords: Atherosclerosis; Carotid intima-media thickness; apolipoproteins; carotid arteries; stroke.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
ApoB/ApoA-I ratio is independently associated with carotid atherosclerosis in type 2 diabetes mellitus with well-controlled LDL cholesterol levels.Korean J Intern Med. 2018 Jan;33(1):138-147. doi: 10.3904/kjim.2017.396. Epub 2017 Dec 28. Korean J Intern Med. 2018. PMID: 29334727 Free PMC article.
-
Association between Apolipoproteins AI and B and Ultrasound Indicators of Carotid Atherosclerosis.Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2018;16(4):376-384. doi: 10.2174/1570161115666171010123157. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29032752
-
Association of carotid intima-media thickness with leptin and apoliprotein b/apoliprotein a-I ratio reveals imminent predictors of subclinical atherosclerosis in psoriasis patients.Acta Medica (Hradec Kralove). 2014;57(1):21-7. doi: 10.14712/18059694.2014.4. Acta Medica (Hradec Kralove). 2014. PMID: 25006659
-
Assessment of Periodontal Status Based on Carotid Artery Intima Media Thickness.Oral Health Prev Dent. 2020 Jul 4;18(3):511-519. doi: 10.3290/j.ohpd.a44036. Oral Health Prev Dent. 2020. PMID: 32515422 Free PMC article.
-
Meta-analysis of the correlation between serum uric acid level and carotid intima-media thickness.PLoS One. 2021 Feb 11;16(2):e0246416. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0246416. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33571245 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Search for Reliable Circulating Biomarkers to Predict Carotid Plaque Vulnerability.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 3;21(21):8236. doi: 10.3390/ijms21218236. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33153204 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Carotid intima media thickness (CIMT) in adults in the AWI-Gen Nairobi site study: Profiles and predictors.Hipertens Riesgo Vasc. 2023 Jan-Mar;40(1):5-15. doi: 10.1016/j.hipert.2022.08.001. Epub 2022 Sep 21. Hipertens Riesgo Vasc. 2023. PMID: 36153304 Free PMC article.
-
Role of erythrocyte sedimentation rate in ischemic stroke as an inflammatory marker of carotid atherosclerosis.J Neurosci Rural Pract. 2014 Jan;5(1):40-5. doi: 10.4103/0976-3147.127870. J Neurosci Rural Pract. 2014. PMID: 24741248 Free PMC article.
-
Apolipoproteins B and A1 in Ischemic Stroke Subtypes.J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2020 Apr;29(4):104670. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2020.104670. Epub 2020 Feb 10. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2020. PMID: 32057650 Free PMC article.
-
Soluble ST2 is associated with increased carotid intima-media thickness in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A case-control study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Jan;99(5):e18940. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000018940. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 32000412 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yang X, So WY, Kong AP, Ho CS, Lam CW, Stevens RJ, et al. Development and validation of stroke risk equation for Hong Kong Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes: The Hong Kong Diabetes Registry. Diabetes Care. 2007;30:65–70. - PubMed
-
- Lanktree MB, Hegele RA, Yusuf S, Anand SS. Multi-ethnic genetic association study of carotid intima-media thickness using a targeted cardiovascular SNP microarray. Stroke. 2009;40:3173–9. - PubMed
-
- Prati P, Tosetto A, Vanuzzo D, Bader G, Casaroli M, Canciani L, et al. Carotid intima media thickness and plaques can predict the occurrence of ischemic cerebrovascular events. Stroke. 2008;39:2470–6. - PubMed
-
- Johnsen SH, Mathiesen EB, Joakimsen O, Stensland E, Wilsgaard T, Lochen ML, et al. Carotid atherosclerosis is a stronger predictor of myocardial infarction in women than in men: A 6-year follow-up study of 6226 persons: The Tromso Study. Stroke. 2007;38:2873–80. - PubMed
-
- Amato M, Montorsi P, Ravani A, Oldani E, Galli S, Ravagnani PM, et al. Carotid intima-media thickness by B-mode ultrasound as surrogate of coronary atherosclerosis: Correlation with quantitative coronary angiography and coronary intravascular ultrasound findings. Eur Heart J. 2007;28:2094–101. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous