Pemphigus Foliaceus Associated with Psoriasis during the Course of Narrow-Band UVB Therapy: A Simple Coincidence?
- PMID: 22346257
- PMCID: PMC3276776
- DOI: 10.5021/ad.2011.23.S3.S281
Pemphigus Foliaceus Associated with Psoriasis during the Course of Narrow-Band UVB Therapy: A Simple Coincidence?
Abstract
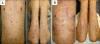
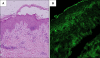
Although psoriasis and bullous diseases are considered to be completely different disease entities, the literature has reported a few cases of psoriasis associated with bullous diseases, most of which are bullous pemphigoid. In limited cases, pemphigus foliaceus has also been reported in association with psoriasis. In most of them, pemphigus lesions usually developed on an untreated patient with a chronic history of psoriasis. Herein, we report a case of 53-year-old male with a chronic history of psoriasis who first developed generalized erosive lesions after 26 cycles of narrow-band ultraviolet B (NBUVB) therapy. A diagnosis of pemphigus foliaceus was made based on skin biopsy and direct immunofluorescence assay. Pemphigus lesions were well controlled with combination therapy of oral steroid and azathioprine. This is the first case where pemphigus foliaceus co-occurred with psoriasis during NBUVB therapy.
Keywords: Narrow-band UVB; Pemphigus foliaceus; Psoriasis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Juvenile Pemphigus Foliaceus in a Patient With Psoriasis Receiving Narrow-Band Ultraviolet-B: Successful Treatment With Rituximab.J Drugs Dermatol. 2023 Aug 1;22(8):830-831. doi: 10.36849/jdd.7241. J Drugs Dermatol. 2023. PMID: 37556511
-
Development of pemphigus foliaceus in a patient with psoriasis: a simple coincidence?Eur J Dermatol. 1998 Jan-Feb;8(1):56-9. Eur J Dermatol. 1998. PMID: 9649683
-
Pemphigus foliaceus with pustular presentation in a patient with psoriasis.An Bras Dermatol. 2017;92(5 Suppl 1):115-117. doi: 10.1590/abd1806-4841.20175709. An Bras Dermatol. 2017. PMID: 29267466 Free PMC article.
-
Dual diagnosis of Pemphigus and pemphigoid. Retrospective review of thirty cases in the literature.Dermatology. 2001;202(4):293-301. doi: 10.1159/000051661. Dermatology. 2001. PMID: 11455140 Review.
-
Diagnosis and classification of pemphigus and bullous pemphigoid.Autoimmun Rev. 2014 Apr-May;13(4-5):477-81. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2014.01.011. Epub 2014 Jan 11. Autoimmun Rev. 2014. PMID: 24424192 Review.
Cited by
-
The coexistence of pemphigus and psoriasis: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Immunol Res. 2019 Feb;67(1):134-141. doi: 10.1007/s12026-018-9031-6. Immunol Res. 2019. PMID: 30338449
-
Interaction of Psoriasis and Bullous Diseases.Front Med (Lausanne). 2018 Aug 8;5:222. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2018.00222. eCollection 2018. Front Med (Lausanne). 2018. PMID: 30135860 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The desmosomal protein desmoglein 1 aids recovery of epidermal differentiation after acute UV light exposure.J Invest Dermatol. 2014 Aug;134(8):2154-2162. doi: 10.1038/jid.2014.124. Epub 2014 Mar 4. J Invest Dermatol. 2014. PMID: 24594668 Free PMC article.
-
Current biologics in treatment of pemphigus foliaceus: a systematic review.Front Immunol. 2023 Oct 12;14:1267668. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1267668. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37901249 Free PMC article.
-
Mycosis fungoides patient accompanied actinic keratosis, actinic keratosis with squamous cell carcinoma transformation, and porokeratosis after NBUVB therapy - 1st case report and review of the literature.Medicine (Baltimore). 2016 Oct;95(41):e5043. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000005043. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016. PMID: 27741114 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bloom D. Psoriasis with superimposed bullous eruption. Med J Rec. 1929;130:246.
-
- Lee CW, Ro YS, Kim JH, Kim JH. Concurrent development of pemphigus foliaceus and psoriasis. Int J Dermatol. 1985;24:316–317. - PubMed
-
- Aghassi D, Dover JS. Pemphigus foliaceus induced by psoralen-UV-A. Arch Dermatol. 1998;134:1300–1301. - PubMed
-
- Tomasini D, Cerri A, Cozzani E, Berti E. Development of pemphigus foliaceus in a patient with psoriasis: a simple coincidence? Eur J Dermatol. 1998;8:56–59. - PubMed
-
- Perez GL, Agger WA, Abellera RM, Dahlberg P. Pemphigus foliaceus coexisting with IgA nephropathy in a patient with psoriasis vulgaris. Int J Dermatol. 1995;34:794–796. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

