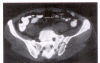
Sacroiliitis and septicemia caused by Campylobacter rectus and Actinomyces odontolyticus
- PMID: 22346489
- PMCID: PMC3250820
- DOI: 10.1155/1994/318928
Sacroiliitis and septicemia caused by Campylobacter rectus and Actinomyces odontolyticus
Abstract
Campylobacter rectus, formerly known as Wolinella recta, is an anaerobic Gram-negative bacillus, generally recognized as an agent responsible for severe periodontitis; only two cases of extra-oral infections have been reported. The first case of septicemia with C rectus and Actinomyces odontolyticus is described in a 37-year-old farmer who suffered from severe sacroiliitis. Also presented are a review of C rectus in human pathology, and a brief review of pyogenic sacroiliitis, a rather rare disease.
Campylobacter rectus, que l’on appelait auparavant Wolinella recta, est un bacille gram négatif anaérobie qui est reconnu comme un agent étiologique de périodontite sévère; seulement deux cas d’infection originant hors de la cavité buccale ont été publiés. Nous rapportons le premier cas de septicémie à C rectus et Actinomyces odontolyticus chez un fermier de 37 ans qui a présenté une sacro-iléite sévère. Nous présentons également une revue de la pathogénicité humaine de C rectus et une brève revue de la sacro-iléite infectieuse, une maladie plutôt rare de nos jours.
Keywords: Actinomyces odontolyticus; Campylobacter rectus; Pyogenic sacroiliitis.
Figures
References
-
- Summanen P. Recent taxonomic changes for anaerobic Gram-positive and selected Gram-negative organisms. Rev Infect Dis. 1993;16(Suppl 4):S168–74. - PubMed
-
- Tanner ACR, Badger S, Lai C-H, Listgarten MA, Visconti RA, Socransky SS. Wolinella gen. nov., Wolinella succinogenes (Vibrio succinogenes Wolin et al) comb. nov., and description of Bacteroides gracilis sp. nov., Wolinella recta sp. nov., Campylobacter consisus sp. nov., and Eikenella corrodens from humans with periodontal disease. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1981;31:432–45.
-
- Tanner A, Stillman N. Oral and dental infections with anaerobic bacteria: clinical features, predominant pathogens and treatment. Clin Infect Dis. 1993;16(Suppl 4):S304–9. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources