Electroanalytical sensors and devices for multiplexed detection of foodborne pathogen microorganisms
- PMID: 22346711
- PMCID: PMC3274141
- DOI: 10.3390/s90705503
Electroanalytical sensors and devices for multiplexed detection of foodborne pathogen microorganisms
Abstract
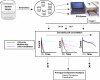
The detection and identification of pathogen microorganisms still rely on conventional culturing techniques, which are not suitable for on-site monitoring. Therefore, a great research challenge in this field is focused on the need to develop rapid, reliable, specific, and sensitive methods to detect these bacteria at low cost. Moreover, the growing interest in biochip development for large scale screening analysis implies improved miniaturization, reduction of analysis time and cost, and multi-analyte detection, which has nowadays become a crucial challenge. This paper reviews multiplexed foodborne pathogen microorganisms detection methods based on electrochemical sensors incorporating microarrays and other platforms. These devices usually involve antibody-antigen and DNA hybridization specific interactions, although other approaches such as the monitoring of oxygen consumption are also considered.
Keywords: electrochemical sensors; multiple detection; pathogen microorganisms.
Figures

References
-
- Lazcka O., Del Campo F.J., Muñoz F.X. Pathogen detection: a perspective of traditional methods and biosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007;22:1205–1217. - PubMed
-
- Goldschmidt M.C. The use of biosensor and microarray techniques in the rapid detection and identification of Salmonellae. J. AOAC Int. 2006;89:530–537. - PubMed
-
- Sadik O.A., Aluoch A.O., Zhou A. Status of biomolecular biorecognition using electrochemical techniques. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009;24:2749–2765. - PubMed
-
- Palchetti I., Mascini M. Electroanalytical biosensors and their potential for food pathogen and toxin detection. Anal. Bioanaly. Chem. 2008;391:455–471. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

