Waveguide-based biosensors for pathogen detection
- PMID: 22346727
- PMCID: PMC3274158
- DOI: 10.3390/s90705783
Waveguide-based biosensors for pathogen detection
Abstract
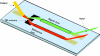
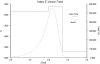
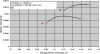
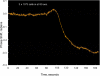
Optical phenomena such as fluorescence, phosphorescence, polarization, interference and non-linearity have been extensively used for biosensing applications. Optical waveguides (both planar and fiber-optic) are comprised of a material with high permittivity/high refractive index surrounded on all sides by materials with lower refractive indices, such as a substrate and the media to be sensed. This arrangement allows coupled light to propagate through the high refractive index waveguide by total internal reflection and generates an electromagnetic wave-the evanescent field-whose amplitude decreases exponentially as the distance from the surface increases. Excitation of fluorophores within the evanescent wave allows for sensitive detection while minimizing background fluorescence from complex, "dirty" biological samples. In this review, we will describe the basic principles, advantages and disadvantages of planar optical waveguide-based biodetection technologies. This discussion will include already commercialized technologies (e.g., Corning's EPIC(®) Ô, SRU Biosystems' BIND(™), Zeptosense(®), etc.) and new technologies that are under research and development. We will also review differing assay approaches for the detection of various biomolecules, as well as the thin-film coatings that are often required for waveguide functionalization and effective detection. Finally, we will discuss reverse-symmetry waveguides, resonant waveguide grating sensors and metal-clad leaky waveguides as alternative signal transducers in optical biosensing.
Keywords: biosensors; fluorescence; immunoassay; pathogen sensor; planar optical waveguides; thin film.
Figures





References
-
- Rowe-Taitt C., Anderson G., Lingerfelt B., Feldstein M., Ligler F. Nine-Analyte Detection Using an Array-based Biosensor. Anal. Chem. 2002;74:6114–6120. - PubMed
-
- Plowman T.E., Durstchi J., Wang H., Christensen D., Heron J., Reichert W. Multi-Analyte Fluoroimmunoassay Using an Integrated Optical Waveguide Sensor. Anal. Chem. 1999;71:4344–4352. - PubMed
-
- Lukosz W., Tiefenthaler K. Directional Switching in Planar Waveguides Effected by Absorbtion-Desorbtion Processes. Institution of Electrical Engineers. 2nd European Conference of Integrated Optics; Florence, Italy. October 17–18; 1983. pp. 152–155. Conference Publication No. 227,
-
- Lukosz W., Tiefenthaler K. Integrated Optical Chemical and Direct Biochemical Sensors. Sens. Actuators B. 1995;29:37–50.
-
- Nishihara H., Haruna M., Suhara T. Optical Integrated Circuits. McGraw-Hill Book Company; New York, NY, USA: 1985. pp. 41–49.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

