The Arabidopsis lectin receptor kinase LecRK-V.5 represses stomatal immunity induced by Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000
- PMID: 22346749
- PMCID: PMC3276567
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002513
The Arabidopsis lectin receptor kinase LecRK-V.5 represses stomatal immunity induced by Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000
Abstract
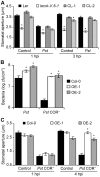
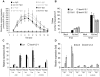
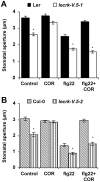
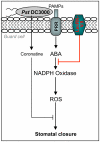
Stomata play an important role in plant innate immunity by limiting pathogen entry into leaves but molecular mechanisms regulating stomatal closure upon pathogen perception are not well understood. Here we show that the Arabidopsis thaliana L-type lectin receptor kinase-V.5 (LecRK-V.5) negatively regulates stomatal immunity. Loss of LecRK-V.5 function increased resistance to surface inoculation with virulent bacteria Pseudomonas syringae pv tomato DC3000. Levels of resistance were not affected after infiltration-inoculation, suggesting that LecRK-V.5 functions at an early defense stage. By contrast, lines overexpressing LecRK-V.5 were more susceptible to Pst DC3000. Enhanced resistance in lecrk-V.5 mutants was correlated with constitutive stomatal closure, while increased susceptibility phenotypes in overexpression lines were associated with early stomatal reopening. Lines overexpressing LecRK-V.5 also demonstrated a defective stomatal closure after pathogen-associated molecular pattern (PAMP) treatments. LecRK-V.5 is rapidly expressed in stomatal guard cells after bacterial inoculation or treatment with the bacterial PAMP flagellin. In addition, lecrk-V.5 mutants guard cells exhibited constitutive accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and inhibition of ROS production opened stomata of lecrk-V.5. LecRK-V.5 is also shown to interfere with abscisic acid-mediated stomatal closure signaling upstream of ROS production. These results provide genetic evidences that LecRK-V.5 negatively regulates stomatal immunity upstream of ROS biosynthesis. Our data reveal that plants have evolved mechanisms to reverse bacteria-mediated stomatal closure to prevent long-term effect on CO(2) uptake and photosynthesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Disease resistance to Pectobacterium carotovorum is negatively modulated by the Arabidopsis Lectin Receptor Kinase LecRK-V.5.Plant Signal Behav. 2012 Sep 1;7(9):1070-2. doi: 10.4161/psb.21013. Epub 2012 Aug 17. Plant Signal Behav. 2012. PMID: 22899085 Free PMC article.
-
Nonredundant functions of Arabidopsis LecRK-V.2 and LecRK-VII.1 in controlling stomatal immunity and jasmonate-mediated stomatal closure.New Phytol. 2018 Apr;218(1):253-268. doi: 10.1111/nph.14953. Epub 2017 Dec 18. New Phytol. 2018. PMID: 29250804
-
The lectin receptor kinase-VI.2 is required for priming and positively regulates Arabidopsis pattern-triggered immunity.Plant Cell. 2012 Mar;24(3):1256-70. doi: 10.1105/tpc.112.095778. Epub 2012 Mar 16. Plant Cell. 2012. PMID: 22427336 Free PMC article.
-
New approaches to the biology of stomatal guard cells.Plant Cell Physiol. 2014 Feb;55(2):241-50. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pct145. Epub 2013 Oct 7. Plant Cell Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24104052 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of stomata in plant innate immunity and foliar bacterial diseases.Annu Rev Phytopathol. 2008;46:101-22. doi: 10.1146/annurev.phyto.121107.104959. Annu Rev Phytopathol. 2008. PMID: 18422426 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Lectin receptor kinases in plant innate immunity.Front Plant Sci. 2013 May 7;4:124. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2013.00124. eCollection 2013. Front Plant Sci. 2013. PMID: 23675375 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of global change factors on redox signaling underpinning stress tolerance.Plant Physiol. 2013 Jan;161(1):5-19. doi: 10.1104/pp.112.205690. Epub 2012 Nov 14. Plant Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23151347 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
The Arabidopsis thaliana lectin receptor kinase LecRK-I.9 is required for full resistance to Pseudomonas syringae and affects jasmonate signalling.Mol Plant Pathol. 2017 Sep;18(7):937-948. doi: 10.1111/mpp.12457. Epub 2016 Sep 15. Mol Plant Pathol. 2017. PMID: 27399963 Free PMC article.
-
STRESS INDUCED FACTOR 2 Regulates Arabidopsis Stomatal Immunity through Phosphorylation of the Anion Channel SLAC1.Plant Cell. 2020 Jul;32(7):2216-2236. doi: 10.1105/tpc.19.00578. Epub 2020 Apr 23. Plant Cell. 2020. PMID: 32327536 Free PMC article.
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinases MPK3 and MPK6 phosphorylate receptor-like cytoplasmic kinase CDL1 to regulate soybean basal immunity.Plant Cell. 2024 Mar 29;36(4):963-986. doi: 10.1093/plcell/koae008. Plant Cell. 2024. PMID: 38301274 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boller T, Felix G. A renaissance of elicitors: perception of microbe-associated molecular patterns and danger signals by pattern-recognition receptors. Annu Rev Plant Biol. 2009;60:379–406. - PubMed
-
- Acharya BR, Assmann SM. Hormone interactions in stomatal function. Plant Mol Biol. 2009;69:451–462. - PubMed
-
- Melotto M, Underwood W, Koczan J, Nomura K, He S-Y. Plant stomata function in innate immunity against bacterial invasion. Cell. 2006;126:969–980. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

