CKD-712, (S)-1-(α-naphthylmethyl)-6,7-dihydroxy-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline, Inhibits the NF-κB Activation and Augments Akt Activation during TLR4 Signaling
- PMID: 22346785
- PMCID: PMC3275714
- DOI: 10.4110/in.2011.11.6.420
CKD-712, (S)-1-(α-naphthylmethyl)-6,7-dihydroxy-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline, Inhibits the NF-κB Activation and Augments Akt Activation during TLR4 Signaling
Abstract
Since CKD-712 has been developed as an anti-inflammatory agent, we examined the effect of CKD-712 during TLR4 signaling. Using HEK293 cells expressing TLR4, CKD-712 was pre-treated 1 hr before LPS stimulation. Activation of NF-κB was assessed by promoter assay. The activation of ERK, JNK, p38, IRF3 and Akt was measured by western blotting. CKD-712 inhibited the NF-κB signaling triggered by LPS. The activation of ERK, JNK, p38 or IRF3 was not inhibited by CKD-712. On the contrary the activation of these molecules was augmented slightly. The activation of Akt with stimulation of LPS was also enhanced with CKD-712 pre-treatment at lower concentration, but was inhibited at higher concentration. We suggest that during TLR4 signaling CKD-712 inhibits NF-κB activation. However, CKD-712 augmented the activation of Akt as well as Map kinases. Therefore, we suggest that CKD-712 might have a role as an immunomodulator.
Keywords: Akt; CKD-712; TLR4; immunomodulator.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflict of interest.
Figures


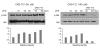
References
-
- Clermont G, Angus DC, Kalassian KG, Linde-Zwirble WT, Ramakrishnan N, Linden PK, Pinsky MR. Reassessing the value of short-term mortality in sepsis: comparing conventional approaches to modeling. Crit Care Med. 2003;31:2627–2633. - PubMed
-
- Poltorak A, He X, Smirnova I, Liu MY, Van Huffel C, Du X, Birdwell D, Alejos E, Silva M, Galanos C, Freudenberg M, Ricciardi-Castagnoli P, Layton B, Beutler B. Defective LPS signaling in C3H/HeJ and C57BL/10ScCr mice: mutations in Tlr4 gene. Science. 1998;282:2085–2088. - PubMed
-
- Schwandner R, Dziarski R, Wesche H, Rothe M, Kirschning CJ. Peptidoglycan- and lipoteichoic acid-induced cell activation is mediated by toll-like receptor 2. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:17406–17409. - PubMed
-
- Flo TH, Halaas O, Lien E, Ryan L, Teti G, Golenbock DT, Sundan A, Espevik T. Human toll-like receptor 2 mediates monocyte activation by Listeria monocytogenes, but not by group B streptococci or lipopolysaccharide. J Immunol. 2000;164:2064–2069. - PubMed
-
- Tamandl D, Bahrami M, Wessner B, Weigel G, Ploder M, Fürst W, Roth E, Boltz-Nitulescu G, Spittler A. Modulation of toll-like receptor 4 expression on human monocytes by tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-6: tumor necrosis factor evokes lipopolysaccharide hyporesponsiveness, whereas interleukin-6 enhances lipopolysaccharide activity. Shock. 2003;20:224–229. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

