N-Benzoyl-2-nitro-benzene-sulfonamide
- PMID: 22346969
- PMCID: PMC3275024
- DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811055917
N-Benzoyl-2-nitro-benzene-sulfonamide
Abstract
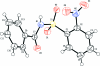
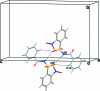
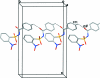
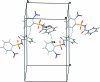
In the title compound, C(13)H(10)N(2)O(5)S, the N-C bond in the C-SO(2)-NH-C segment has gauche torsion angles with respect to the S=O bonds. The conformation between the N-H bond and the ortho-nitro group in the sulfonyl benzene ring is syn. The mol-ecule is twisted at the S-N bond with a torsion angle of -63.4 (2)°. The sulfonyl benzene ring is tilted by 77.1 (1)° relative to the -SO(2)-NH-C-O segment. The dihedral angle between the sulfonyl and the benzoyl benzene rings is 88.6 (1)°. In the crystal, pairs of N-H⋯O(S) hydrogen bonds link the mol-ecules into inversion dimers, which are linked by weak C-H⋯O and C-H⋯π inter-actions along the b axis.
Figures
References
-
- Bowes, K. F., Glidewell, C., Low, J. N., Skakle, J. M. S. & Wardell, J. L. (2003). Acta Cryst. C59, o1–o3. - PubMed
-
- Gowda, B. T., Jyothi, K., Kozisek, J. & Fuess, H. (2003). Z. Naturforsch. Teil A, 58, 656–660.
-
- Gowda, B. T., Kozisek, J. & Fuess, H. (2006). Z. Naturforsch. Teil A, 61, 588–594.
-
- Gowda, B. T. & Mahadevappa, D. S. (1983). Talanta, 30, 359–362. - PubMed
-
- Jayalakshmi, K. L. & Gowda, B. T. (2004). Z. Naturforsch. Teil A, 59, 491–500.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
