Intra operative indocyanine green video-angiography in cerebrovascular surgery: An overview with review of literature
- PMID: 22347330
- PMCID: PMC3277076
- DOI: 10.4103/1793-5482.92168
Intra operative indocyanine green video-angiography in cerebrovascular surgery: An overview with review of literature
Abstract
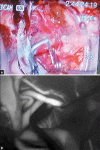
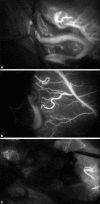
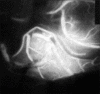
Microscope integrated Near infra red Indocyanine green video angiography (NIR ICG VA) has been frequently used in cerebrovascular surgery. It is believed to be a simple and reliable method with acquisition of real time high spatial resolution images. The aim of this review article was to evaluate the efficacy of intra operative Indocyanine green video angiography (ICG VA) in Aneurysm, brain arteriovenous malformations (AVM) and extracranial-intracranial (EC-IC) bypass surgeries and also to analyze its limitations. Intra operative imaging is a very useful tool in guiding surgery; thus, avoiding surgical morbidity. Now-a-days, many cerebrovascular units are using ICG VA rather than Doppler and intra operative DSA in most of their aneurysm surgeries, and surgeons are incorporating this technique for AVM and in EC-IC bypass surgeries too. This article is an overview of the beneficial effects of ICG VA in cerebrovascular surgery and will also point out its limitations in various circumstances. Intra operative ICG VA gives high resolution, real time images of arterial, capillary, and venous flow of cerebral vasculature. Although it gives adequate information about the clipped neck, parent/branching artery and perforator involvement, it has some limitations like viewing the neck residuals located behind the aneurysm, thick walled atherosclerotic vessels, and thrombosed aneurysms. In AVM surgery, it is useful in detecting the residual nidus in diffuse type AVM, but cannot be relied in deep seated AVMs and it gives exact information about the anastomosis site in EC-IC bypass, thus, avoiding early bypass graft failure. NIR ICG VA is a simple, reliable, and quick method to pick up subtle findings in cerebrovascular procedures. But in selected cases of aneurysms, endoscopy and intra operative Digital substraction angiography (DSA) may be helpful, whereas in deep seated AVMs, navigation may be required as an adjunct to confirm intra operative findings.
Keywords: Aneurysms; arteriovenous malformations; cerebral revascularization; extracranial-intracranial bypass; indocyanine green; video angiography.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Raabe A, Beck J, Gerlach R, Zimmermann M, Seifert V. Near infrared Indocyanine green video angiography - A new method for intra operative assessment of vascular flow. Neurosurgery. 2003;52:132–9. - PubMed
-
- Raabe A, Nakaji P, Beck J, Kim LJ, Hsu FP, Kammerman JD, et al. Prospective evaluation of surgical microscope integrated intra operative near infrared Indocyanine green video angiography during aneurysm surgery. J Neurosurgery. 2005;103:982–9. - PubMed
-
- Park DH, Kang SH, Lee JB, Lim DJ, Kwon TH, Chung YG, et al. Angiographic features, Surgical management ad outcomes of proximal middle cerebral artery aneurysms. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2008;110:544–51. - PubMed
-
- Sharma BS, Gupta A, Ahmed FU, Suri A, Mehta VS. Surgical management of giant intracranial aneurysms. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2008;110:674–81. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

