Cellular growth kinetics distinguish a cyclophilin inhibitor from an HSP90 inhibitor as a selective inhibitor of hepatitis C virus
- PMID: 22347373
- PMCID: PMC3275588
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030286
Cellular growth kinetics distinguish a cyclophilin inhibitor from an HSP90 inhibitor as a selective inhibitor of hepatitis C virus
Abstract
During antiviral drug discovery, it is critical to distinguish molecules that selectively interrupt viral replication from those that reduce virus replication by adversely affecting host cell viability. In this report we investigate the selectivity of inhibitors of the host chaperone proteins cyclophilin A (CypA) and heat-shock protein 90 (HSP90) which have each been reported to inhibit replication of hepatitis C virus (HCV). By comparing the toxicity of the HSP90 inhibitor, 17-(Allylamino)-17-demethoxygeldanamycin (17-AAG) to two known cytostatic compounds, colchicine and gemcitabine, we provide evidence that 17-AAG exerts its antiviral effects indirectly through slowing cell growth. In contrast, a cyclophilin inhibitor, cyclosporin A (CsA), exhibited selective antiviral activity without slowing cell proliferation. Furthermore, we observed that 17-AAG had little antiviral effect in a non-dividing cell-culture model of HCV replication, while CsA reduced HCV titer by more than two orders of magnitude in the same model. The assays we describe here are useful for discriminating selective antivirals from compounds that indirectly affect virus replication by reducing host cell viability or slowing cell growth.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




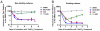
Similar articles
-
The Novel Cyclophilin Inhibitor CPI-431-32 Concurrently Blocks HCV and HIV-1 Infections via a Similar Mechanism of Action.PLoS One. 2015 Aug 11;10(8):e0134707. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0134707. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26263487 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the anti-hepatitis C virus effects of cyclophilin inhibitors, cyclosporin A, and NIM811.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006 May 12;343(3):879-84. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.03.059. Epub 2006 Mar 29. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006. PMID: 16564500
-
Combination therapy for hepatitis C virus with heat-shock protein 90 inhibitor 17-AAG and proteasome inhibitor MG132.Antivir Chem Chemother. 2010 Mar 9;20(4):161-7. doi: 10.3851/IMP1479. Antivir Chem Chemother. 2010. PMID: 20231781
-
Chemical genetics approach to hepatitis C virus replication: cyclophilin as a target for anti-hepatitis C virus strategy.Rev Med Virol. 2007 Jul-Aug;17(4):245-52. doi: 10.1002/rmv.534. Rev Med Virol. 2007. PMID: 17299803 Review.
-
Cyclophilin inhibitors.Clin Liver Dis. 2009 Aug;13(3):403-17. doi: 10.1016/j.cld.2009.05.002. Clin Liver Dis. 2009. PMID: 19628157 Review.
Cited by
-
Selected nucleos(t)ide-based prescribed drugs and their multi-target activity.Eur J Pharmacol. 2019 Dec 15;865:172747. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2019.172747. Epub 2019 Oct 18. Eur J Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31634460 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A small-molecule inhibitor of hepatitis C virus infectivity.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014;58(1):386-96. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02083-13. Epub 2013 Oct 28. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014. PMID: 24165192 Free PMC article.
-
Stress proteins: the biological functions in virus infection, present and challenges for target-based antiviral drug development.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020 Jul 13;5(1):125. doi: 10.1038/s41392-020-00233-4. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020. PMID: 32661235 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in the Development of Antiviral Compounds for Rotavirus Infections.mBio. 2021 May 11;12(3):e00111-21. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00111-21. mBio. 2021. PMID: 33975930 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Drug repurposing of pyrimidine analogs as potent antiviral compounds against human enterovirus A71 infection with potential clinical applications.Sci Rep. 2020 May 18;10(1):8159. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-65152-4. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32424333 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Reichard O, Schvarcz R, Weiland O. Therapy of hepatitis C: alpha interferon and ribavirin. Hepatology. 1997;26:108S–111S. - PubMed
-
- Patel H, Heathcote EJ. Sustained virological response with 29 days of Debio 025 monotherapy in hepatitis C virus genotype 3. Gut. 2010;58:1644–1653. - PubMed
-
- Le Pogam S, Seshaadri A, Ewing A, Kang H, Kosaka A, et al. RG7128 alone or in combination with pegylated interferon-alpha2a and ribavirin prevents hepatitis C virus (HCV) Replication and selection of resistant variants in HCV-infected patients. J Infect Dis. 2010;202:1510–1519. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

