Caffeic acid phenethyl ester and its amide analogue are potent inhibitors of leukotriene biosynthesis in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes
- PMID: 22347509
- PMCID: PMC3276500
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0031833
Caffeic acid phenethyl ester and its amide analogue are potent inhibitors of leukotriene biosynthesis in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes
Abstract
Background: 5-lipoxygenase (5-LO) catalyses the transformation of arachidonic acid (AA) into leukotrienes (LTs), which are important lipid mediators of inflammation. LTs have been directly implicated in inflammatory diseases like asthma, atherosclerosis and rheumatoid arthritis; therefore inhibition of LT biosynthesis is a strategy for the treatment of these chronic diseases.
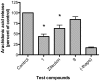
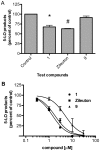
Methodology/principal findings: Analogues of caffeic acid, including the naturally-occurring caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE), were synthesized and evaluated for their capacity to inhibit 5-LO and LTs biosynthesis in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMNL) and whole blood. Anti-free radical and anti-oxidant activities of the compounds were also measured. Caffeic acid did not inhibit 5-LO activity or LT biosynthesis at concentrations up to 10 µM. CAPE inhibited 5-LO activity (IC(50) 0.13 µM, 95% CI 0.08-0.23 µM) more effectively than the clinically-approved 5-LO inhibitor zileuton (IC(50) 3.5 µM, 95% CI 2.3-5.4 µM). CAPE was also more effective than zileuton for the inhibition of LT biosynthesis in PMNL but the compounds were equipotent in whole blood. The activity of the amide analogue of CAPE was similar to that of zileuton. Inhibition of LT biosynthesis by CAPE was the result of the inhibition of 5-LO and of AA release. Caffeic acid, CAPE and its amide analog were free radical scavengers and antioxidants with IC(50) values in the low µM range; however, the phenethyl moiety of CAPE was required for effective inhibition of 5-LO and LT biosynthesis.
Conclusions: CAPE is a potent LT biosynthesis inhibitor that blocks 5-LO activity and AA release. The CAPE structure can be used as a framework for the rational design of stable and potent inhibitors of LT biosynthesis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Structure-activity relationship of caffeic acid phenethyl ester analogs as new 5-lipoxygenase inhibitors.Chem Biol Drug Des. 2017 Apr;89(4):514-528. doi: 10.1111/cbdd.12874. Epub 2016 Nov 15. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2017. PMID: 27717142
-
Novel Oxadiazole-Based Bioisostere of Caffeic Acid Phenethyl Ester: Synthesis, Anticancer Activity, and Inhibition of Lipoxygenase Product Biosynthesis.Drug Dev Res. 2025 May;86(3):e70099. doi: 10.1002/ddr.70099. Drug Dev Res. 2025. PMID: 40320854 Free PMC article.
-
New Hydroxycinnamic Acid Esters as Novel 5-Lipoxygenase Inhibitors That Affect Leukotriene Biosynthesis.Mediators Inflamm. 2017;2017:6904634. doi: 10.1155/2017/6904634. Epub 2017 Jun 7. Mediators Inflamm. 2017. PMID: 28680195 Free PMC article.
-
Caffeic acid phenethyl ester and therapeutic potentials.Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:145342. doi: 10.1155/2014/145342. Epub 2014 May 29. Biomed Res Int. 2014. PMID: 24971312 Free PMC article. Review.
-
5-Lipoxygenase: a target for antiinflammatory drugs revisited.Curr Med Chem. 1999 Jan;6(1):71-85. Curr Med Chem. 1999. PMID: 9873115 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulatory effects of caffeic acid phenethyl ester on neuroinflammation in microglial cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Mar 11;16(3):5572-89. doi: 10.3390/ijms16035572. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 25768341 Free PMC article.
-
Interpretation of the absorbed constituents and pharmacological effect of Spica Schizonepetae extract on non-small cell lung cancer.PLoS One. 2021 Mar 17;16(3):e0248700. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0248700. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33730076 Free PMC article.
-
Caffeic acid phenethyl ester induces adrenoleukodystrophy (Abcd2) gene in human X-ALD fibroblasts and inhibits the proinflammatory response in Abcd1/2 silenced mouse primary astrocytes.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Apr;1831(4):747-58. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2013.01.004. Epub 2013 Jan 11. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23318275 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and antiradical/antioxidant activities of caffeic acid phenethyl ester and its related propionic, acetic, and benzoic acid analogues.Molecules. 2012 Dec 10;17(12):14637-50. doi: 10.3390/molecules171214637. Molecules. 2012. PMID: 23222926 Free PMC article.
-
Phenolic acid phenethylesters and their corresponding ketones: Inhibition of 5-lipoxygenase and stability in human blood and HepaRG cells.Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2019 Sep 13;7(5):e00524. doi: 10.1002/prp2.524. eCollection 2019 Oct. Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2019. PMID: 31523435 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Samuelsson B. Leukotrienes: mediators of immediate hypersensitivity reactions and inflammation. Science. 1983;220:568–575. - PubMed
-
- Mehrabian M, Allayee H, Wong J, Shi W, Wang XP, et al. Identification of 5-lipoxygenase as a major gene contributing to atherosclerosis susceptibility in mice. Circ Res. 2002;91:120–126. - PubMed
-
- Leff JA, Busse WW, Pearlman D, Bronsky EA, Kemp J, et al. Montelukast, a leukotriene-receptor antagonist, for the treatment of mild asthma and exercise-induced bronchoconstriction. N Engl J Med. 1998;339:147–152. - PubMed
-
- Gupta S, Srivastava M, Ahmad N, Sakamoto K, Bostwick DG, et al. Lipoxygenase-5 is overexpressed in prostate adenocarcinoma. Cancer. 2001;91:737–743. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

