Neuroimmune endocrine effects of antidepressants
- PMID: 22347798
- PMCID: PMC3280108
- DOI: 10.2147/NDT.S16409
Neuroimmune endocrine effects of antidepressants
Abstract
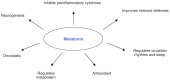
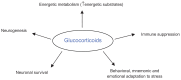
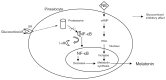
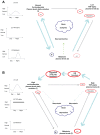
Antidepressant pharmacotherapy is to date the most often used treatment for depression, but the exact mechanism of action underlying its therapeutic effect is still unclear. Many theories have been put forward to account for depression, as well as antidepressant activity, but none of them is exhaustive. Neuroimmune endocrine impairment is found in depressed patients; high levels of circulating corticosteroids along with hyperactivation of the immune system, high levels of proinflammatory cytokines, low levels of melatonin in plasma and urine, and disentrainment of circadian rhythms have been demonstrated. Moreover, antidepressant treatment seems to correct or at least to interfere with these alterations. In this review, we summarize the complex neuroimmune endocrine and chronobiological alterations found in patients with depression and how these systems interact with each other. We also explain how antidepressant therapy can modify these systems, along with some possible mechanisms of action shown in animal and human models.
Keywords: antidepressant agents; biological markers; cytokines; endophenotype; human; neuroinflammation; psychoneuroimmunology.
Figures
References
-
- Kessler RC. Epidemiology of women and depression. J Affect Disord. 2003;74(1):5–13. - PubMed
-
- O’Brien SM, Scott LV, Dinan TG. Cytokines: abnormalities in major depression and implications for pharmacological treatment. Hum Psychopharmacol. 2004;19(6):397–403. - PubMed
-
- Carvalho LA, Pariante CM. In vitro modulation of the glucocorticoid receptor by antidepressants. Stress. 2008;11(6):411–424. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

