EGCG enhances the therapeutic potential of gemcitabine and CP690550 by inhibiting STAT3 signaling pathway in human pancreatic cancer
- PMID: 22348037
- PMCID: PMC3278426
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0031067
EGCG enhances the therapeutic potential of gemcitabine and CP690550 by inhibiting STAT3 signaling pathway in human pancreatic cancer
Abstract
Background: Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 (STAT3) is an oncogene, which promotes cell survival, proliferation, motility and progression in cancer cells. Targeting STAT3 signaling may lead to the development of novel therapeutic approaches for human cancers. Here, we examined the effects of epigallocathechin gallate (EGCG) on STAT3 signaling in pancreatic cancer cells, and assessed the therapeutic potential of EGCG with gemcitabine or JAK3 inhibitor CP690550 (Tasocitinib) for the treatment and/or prevention of pancreatic cancer.
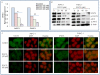
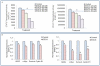
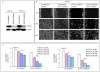
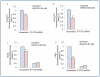
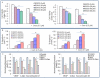
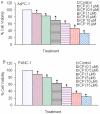
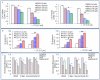
Methodology/principal findings: Cell viability and apoptosis were measured by XTT assay and TUNEL staining, respectively. Gene and protein expressions were measured by qRT-PCR and Western blot analysis, respectively. The results revealed that EGCG inhibited the expression of phospho and total JAK3 and STAT3, STAT3 transcription and activation, and the expression of STAT3-regulated genes, resulting in the inhibition of cell motility, migration and invasion, and the induction of caspase-3 and PARP cleavage. The inhibition of STAT3 enhanced the inhibitory effects of EGCG on cell motility and viability. Additionally, gemcitabine and CP690550 alone inhibited STAT3 target genes and synergized with EGCG to inhibit cell viability and induce apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells.
Conclusions/significance: Overall, these results suggest that EGCG suppresses the growth, invasion and migration of pancreatic cancer cells, and induces apoptosis by interfering with the STAT3 signaling pathway. Moreover, EGCG further enhanced the therapeutic potential of gemcitabine and CP690550 against pancreatic cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Schindler C, Darnell JE. Transcriptional Responses to Polypeptide Ligands: The JAK-STAT Pathway. Annual Review of Biochemistry. 1995;64:621–652. - PubMed
-
- Darnell J, Kerr I, Stark G. Jak-STAT pathways and transcriptional activation in response to IFNs and other extracellular signaling proteins. Science. 1994;264:1415–1421. - PubMed
-
- Darnell JE. STATs and Gene Regulation. Science. 1997;277:1630–1635. - PubMed
-
- Darnell JE., Jr Transcription factors as targets for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2:740–749. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

