Expression of calmodulin and myosin light chain kinase during larval settlement of the Barnacle Balanus amphitrite
- PMID: 22348072
- PMCID: PMC3278446
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0031337
Expression of calmodulin and myosin light chain kinase during larval settlement of the Barnacle Balanus amphitrite
Abstract
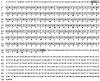
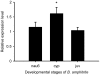
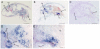
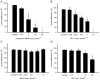
Barnacles are one of the most common organisms in intertidal areas. Their life cycle includes seven free-swimming larval stages and sessile juvenile and adult stages. The transition from the swimming to the sessile stages, referred to as larval settlement, is crucial for their survivor success and subsequent population distribution. In this study, we focused on the involvement of calmodulin (CaM) and its binding proteins in the larval settlement of the barnacle, Balanus ( = Amphibalanus) amphitrite. The full length of CaM gene was cloned from stage II nauplii of B. amphitrite (referred to as Ba-CaM), encoding 149 amino acid residues that share a high similarity with published CaMs in other organisms. Quantitative real-time PCR showed that Ba-CaM was highly expressed in cyprids, the stage at which swimming larvae are competent to attach and undergo metamorphosis. In situ hybridization revealed that the expressed Ba-CaM gene was localized in compound eyes, posterior ganglion and cement glands, all of which may have essential functions during larval settlement. Larval settlement assays showed that both the CaM inhibitor compound 48/80 and the CaM-dependent myosin light chain kinase (MLCK) inhibitor ML-7 effectively blocked barnacle larval settlement, whereas Ca(2+)/CaM-dependent kinase II (CaMKII) inhibitors did not show any clear effects. The subsequent real-time PCR assay showed a higher expression level of Ba-MLCK gene in larval stages than in adults, suggesting an important role of Ba-MLCK gene in larval development and competency. Overall, the results suggest that CaM and CaM-dependent MLCK function during larval settlement of B. amphitrite.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effects of calmodulin inhibitors on cyprid larvae of the barnacle, Balanus amphitrite.J Exp Zool. 1998 Jan 1;280(1):8-17. J Exp Zool. 1998. PMID: 9437848
-
Quantitative proteomics study of larval settlement in the Barnacle Balanus amphitrite.PLoS One. 2014 Feb 13;9(2):e88744. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0088744. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24551147 Free PMC article.
-
The regulatory role of the NO/cGMP signal transduction cascade during larval attachment and metamorphosis of the barnacle Balanus (=Amphibalanus) amphitrite.J Exp Biol. 2012 Nov 1;215(Pt 21):3813-22. doi: 10.1242/jeb.070235. Epub 2012 Aug 1. J Exp Biol. 2012. PMID: 22855617
-
Characterization and expression of calmodulin gene during larval settlement and metamorphosis of the polychaete Hydroides elegans.Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol. 2012 Aug;162(4):113-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpb.2012.04.001. Epub 2012 Apr 5. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22507549
-
Regulation of smooth muscle myosin light chain kinase by calmodulin.Adv Exp Med Biol. 1991;304:11-24. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-6003-2_3. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1991. PMID: 1803894 Review.
Cited by
-
Voltage Dependence of a Neuromodulator-Activated Ionic Current.eNeuro. 2016 May 12;3(2):ENEURO.0038-16.2016. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0038-16.2016. eCollection 2016 Mar-Apr. eNeuro. 2016. PMID: 27257619 Free PMC article.
-
Integrating Gene Transcription-Based Biomarkers to Understand Desert Tortoise and Ecosystem Health.Ecohealth. 2015 Sep;12(3):501-12. doi: 10.1007/s10393-014-0998-8. Epub 2015 Jan 6. Ecohealth. 2015. PMID: 25561383
-
Mode of action of antifouling compound albofungin in inhibiting barnacle larval settlement.iScience. 2023 May 28;26(7):106981. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.106981. eCollection 2023 Jul 21. iScience. 2023. PMID: 37534162 Free PMC article.
-
Monitoring nearshore ecosystem health using Pacific razor clams (Siliqua patula) as an indicator species.PeerJ. 2020 Mar 5;8:e8761. doi: 10.7717/peerj.8761. eCollection 2020. PeerJ. 2020. PMID: 32185117 Free PMC article.
-
Proteome of larval metamorphosis induced by epinephrine in the Fujian oyster Crassostrea angulata.BMC Genomics. 2020 Sep 29;21(1):675. doi: 10.1186/s12864-020-07066-z. BMC Genomics. 2020. PMID: 32993483 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Knight-Jones EW, Crisp D J. Gregariousness in barnacles in relation to the fouling of ships and to anti- fouling research. Nature. 1953;171:1109–1110. - PubMed
-
- Barnes H, Barnes M. Studies on the reproduction of cirripedes. I. Introduction: Copulation, release of oocytes, and formation of the egg lamellae. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol. 1977;27:195–218.
-
- Bernard FJ, Lane CE. Early settlement and metamorphosis of the barnacle Balanus amphitrite niveus. J Morphol. 1962;110:19–39.
-
- Underwood AJ, Fairweather PG. Supply-side ecology and benthic marine assemblages. Trends Ecol Evol. 1989;4:16–20. - PubMed
-
- Clare AS, Thomas R, Rittschof D. Evidence for the involvement of cyclic AMP in the pheromonal modulation of barnacle settlement. J Exp Biol. 1995;198:655–664. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

