Losartan slows pancreatic tumor progression and extends survival of SPARC-null mice by abrogating aberrant TGFβ activation
- PMID: 22348081
- PMCID: PMC3279359
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0031384
Losartan slows pancreatic tumor progression and extends survival of SPARC-null mice by abrogating aberrant TGFβ activation
Abstract
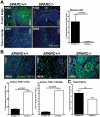
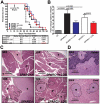
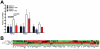
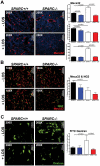
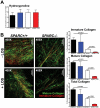
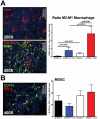
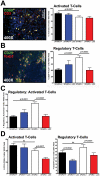
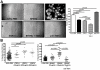
Pancreatic adenocarcinoma, a desmoplastic disease, is the fourth leading cause of cancer-related death in the Western world due, in large part, to locally invasive primary tumor growth and ensuing metastasis. SPARC is a matricellular protein that governs extracellular matrix (ECM) deposition and maturation during tissue remodeling, particularly, during wound healing and tumorigenesis. In the present study, we sought to determine the mechanism by which lack of host SPARC alters the tumor microenvironment and enhances invasion and metastasis of an orthotopic model of pancreatic cancer. We identified that levels of active TGFβ1 were increased significantly in tumors grown in SPARC-null mice. TGFβ1 contributes to many aspects of tumor development including metastasis, endothelial cell permeability, inflammation and fibrosis, all of which are altered in the absence of stromal-derived SPARC. Given these results, we performed a survival study to assess the contribution of increased TGFβ1 activity to tumor progression in SPARC-null mice using losartan, an angiotensin II type 1 receptor antagonist that diminishes TGFβ1 expression and activation in vivo. Tumors grown in SPARC-null mice progressed more quickly than those grown in wild-type littermates leading to a significant reduction in median survival. However, median survival of SPARC-null animals treated with losartan was extended to that of losartan-treated wild-type controls. In addition, losartan abrogated TGFβ induced gene expression, reduced local invasion and metastasis, decreased vascular permeability and altered the immune profile of tumors grown in SPARC-null mice. These data support the concept that aberrant TGFβ1-activation in the absence of host SPARC contributes significantly to tumor progression and suggests that SPARC, by controlling ECM deposition and maturation, can regulate TGFβ availability and activation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Bornstein P. Cell-matrix interactions: the view from the outside. Methods Cell Biol. 2002;69:7–11. - PubMed
-
- Reed MJ, Puolakkainen P, Lane TF, Dickerson D, Bornstein P, et al. Differential expression of SPARC and thrombospondin 1 in wound repair: immunolocalization and in situ hybridization. J Histochem Cytochem. 1993;41:1467–1477. - PubMed
-
- Podhajcer OL, Benedetti LG, Girotti MR, Prada F, Salvatierra E, et al. The role of the matricellular protein SPARC in the dynamic interaction between the tumor and the host. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2008;27:691–705. - PubMed
-
- Pen A, Moreno MJ, Martin J, Stanimirovic DB. Molecular markers of extracellular matrix remodeling in glioblastoma vessels: microarray study of laser-captured glioblastoma vessels. Glia. 2007;55:559–572. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

