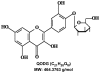
Quercetin-4'-O-β-D-glucopyranoside (QODG) inhibits angiogenesis by suppressing VEGFR2-mediated signaling in zebrafish and endothelial cells
- PMID: 22348123
- PMCID: PMC3278463
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0031708
Quercetin-4'-O-β-D-glucopyranoside (QODG) inhibits angiogenesis by suppressing VEGFR2-mediated signaling in zebrafish and endothelial cells
Abstract
Background: Angiogenesis plays an important role in many physiological and pathological processes. Identification of small molecules that block angiogenesis and are safe and affordable has been a challenge in drug development. Hypericum attenuatum Choisy is a Chinese herb medicine commonly used for treating hemorrhagic diseases. The present study investigates the anti-angiogenic effects of quercetin-4'-O-β-D-glucopyranoside (QODG), a flavonoid isolated from Hypericum attenuatum Choisy, in vivo and in vitro, and clarifies the underlying mechanism of the activity.
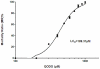
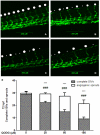
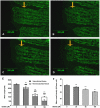
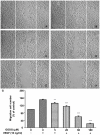
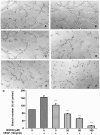
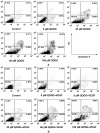
Methodology/principal findings: Tg(fli1:EGFP) transgenic zebrafish embryos were treated with different concentrations of quercetin-4'-O-β-D-glucopyranoside (QODG) (20, 60, 180 µM) from 6 hours post fertilisation (hpf) to 72 hpf, and adult zebrafish were allowed to recover in different concentrations of QODG (20, 60, 180 µM) for 7 days post amputation (dpa) prior morphological observation and angiogenesis phenotypes assessment. Human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) were treated with or without VEGF and different concentrations of QODG (5, 20, 60, 180 µM), then tested for cell viability, cell migration, tube formation and apoptosis. The role of VEGFR2-mediated signaling pathway in QODG-inhibited angiogenesis was evaluated using quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) and Western blotting.
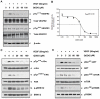
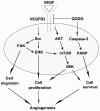
Conclusion/significance: Quercetin-4'-O-β-D-glucopyranoside (QODG) was shown to inhibit angiogenesis in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) in vitro and zebrafish in vivo via suppressing VEGF-induced phosphorylation of VEGFR2. Our results further indicate that QODG inhibits angiogenesis via inhibition of VEGFR2-mediated signaling with the involvement of some key kinases such as c-Src, FAK, ERK, AKT, mTOR and S6K and induction of apoptosis. Together, this study reveals, for the first time, that QODG acts as a potent VEGFR2 kinase inhibitor, and exerts the anti-angiogenic activity at least in part through VEGFR2-mediated signaling pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
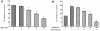
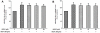
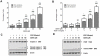
References
-
- Quesada AR, Muñoz-Chápuli R, Medina MA. Anti-angiogenic drugs: from bench to clinical trials. Med Res Rev. 2006;26:483–530. - PubMed
-
- Carmeliet P. Angiogenesis in life, disease and medicine. Nature. 2005;438:932–936. - PubMed
-
- Folkman J. What is the evidence that tumors are angiogenesis dependent? J Natl Cancer Inst. 1990;82:4–6. - PubMed
-
- Eberhard A, Kahlert S, Goede V, Hemmerlein B, Plate KH, et al. Heterogeneity of angiogenesis and blood vessel maturation in human tumors: implications for anti-angiogenic tumor therapies. Cancer Res. 2000;60:1388–1393. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

