Development of protective autoimmunity by immunization with a neural-derived peptide is ineffective in severe spinal cord injury
- PMID: 22348141
- PMCID: PMC3279414
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0032027
Development of protective autoimmunity by immunization with a neural-derived peptide is ineffective in severe spinal cord injury
Abstract
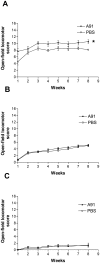
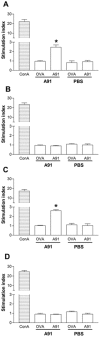
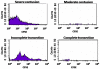
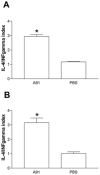
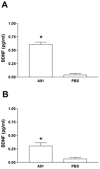
Protective autoimmunity (PA) is a physiological response to central nervous system trauma that has demonstrated to promote neuroprotection after spinal cord injury (SCI). To reach its beneficial effect, PA should be boosted by immunizing with neural constituents or neural-derived peptides such as A91. Immunizing with A91 has shown to promote neuroprotection after SCI and its use has proven to be feasible in a clinical setting. The broad applications of neural-derived peptides make it important to determine the main features of this anti-A91 response. For this purpose, adult Sprague-Dawley rats were subjected to a spinal cord contusion (SCC; moderate or severe) or a spinal cord transection (SCT; complete or incomplete). Immediately after injury, animals were immunized with PBS or A91. Motor recovery, T cell-specific response against A91 and the levels of IL-4, IFN-γ and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) released by A91-specific T (T(A91)) cells were evaluated. Rats with moderate SCC, presented a better motor recovery after A91 immunization. Animals with moderate SCC or incomplete SCT showed significant T cell proliferation against A91 that was characterized chiefly by the predominant production of IL-4 and the release of BDNF. In contrast, immunization with A91 did not promote a better motor recovery in animals with severe SCC or complete SCT. In fact, T cell proliferation against A91 was diminished in these animals. The present results suggest that the effective development of PA and, consequently, the beneficial effects of immunizing with A91 significantly depend on the severity of SCI. This could mainly be attributed to the lack of T(A91) cells which predominantly showed to have a Th2 phenotype capable of producing BDNF, further promoting neuroprotection.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Bakalash S, Kipnis J, Yoles E, Schwartz M. Resistance of retinal ganglion cells to an increase in intraocular pressure is immune-dependent. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2002;43:2648–2653. - PubMed
-
- Ibarra A, Hauben E, Butovsky O, Schwartz M. The therapeutic window after spinal cord injury can accommodate T cell-based vaccination and methylprednisolone in rats. Eur J Neurosci. 2004;19:2984–2990. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

