Neurodevelopmental consequences of sub-clinical carbon monoxide exposure in newborn mice
- PMID: 22348142
- PMCID: PMC3277503
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0032029
Neurodevelopmental consequences of sub-clinical carbon monoxide exposure in newborn mice
Abstract
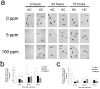
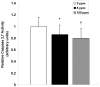
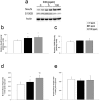
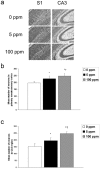
Carbon monoxide (CO) exposure at high concentrations results in overt neurotoxicity. Exposure to low CO concentrations occurs commonly yet is usually sub-clinical. Infants are uniquely vulnerable to a variety of toxins, however, the effects of postnatal sub-clinical CO exposure on the developing brain are unknown. Apoptosis occurs normally within the brain during development and is critical for synaptogenesis. Here we demonstrate that brief, postnatal sub-clinical CO exposure inhibits developmental neuroapoptosis resulting in impaired learning, memory, and social behavior. Three hour exposure to 5 ppm or 100 ppm CO impaired cytochrome c release, caspase-3 activation, and apoptosis in neocortex and hippocampus of 10 day old CD-1 mice. CO increased NeuN protein, neuronal numbers, and resulted in megalencephaly. CO-exposed mice demonstrated impaired memory and learning and reduced socialization following exposure. Thus, CO-mediated inhibition of neuroapoptosis might represent an important etiology of acquired neurocognitive impairment and behavioral disorders in children.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures






References
-
- Kao LW, Nañagas KA. Carbon monoxide poisoning. Emerg Med Clin North Am. 2004;22:985–1018. - PubMed
-
- Smithline HA, Ward KR, Chiulli DA, Blake HC, Rivers EP. Whole body oxygen consumption and critical oxygen delivery in response to prolonged and severe carbon monoxide poisoning. Resuscitation. 2003;56:97–104. - PubMed
-
- Hauck H, Neuberger M. Carbon monoxide uptake and the resulting carboxyhemoglobin in man. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol. 1984;53:186–90. - PubMed
-
- Gorman D, Drewry A, Huang YL, Sames C. The clinical toxicology of carbon monoxide. Toxicology. 2003;187:25–38. - PubMed
-
- Kao LW, Nanagas KA. Carbon monoxide poisoning. Med Clin North Am. 2005;89:1161–1194. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

