Microencapsulated drug delivery: a new approach to pro-inflammatory cytokine inhibition
- PMID: 22348221
- PMCID: PMC3433085
- DOI: 10.3109/02652048.2012.658443
Microencapsulated drug delivery: a new approach to pro-inflammatory cytokine inhibition
Abstract
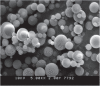
Context: This article reviews the use of albumin microcapsules 3-4 µm in size containing cytokine inhibiting drugs which include neutralizing antibodies to TNF and IL1, CNI-1493, antisense oligonucleotides to TNF and NF-kappaB, and the antioxidant catalase.
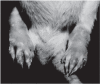
Objective: Describe the effects, cellular uptake and distribution of microencapsulated drugs and the effect in both a peritonitis model of infection and a model of adjuvant-induced arthritis.
Methods: The studies performed by our group are reviewed, the only such studies available.
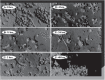
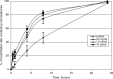
Results: Microencapsulation of these compounds produced high intracellular drug concentrations due to rapid uptake by phagocytic cells, including endothelial cells, without toxicity. All compounds produced excellent inhibition of TNF and IL1 resulting in improved animal survival in a peritonitis model of septic shock and inflammation in an arthritis model.
Conclusion: Albumin microencapsulated pro-inflammatory cytokine inhibiting compounds are superior to equivalent concentration of these compounds administered in solution form.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Microencapsulation of tumor necrosis factor oligomers: a new approach to proinflammatory cytokine inhibition.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2003 Sep;23(9):533-43. doi: 10.1089/10799900360708650. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2003. PMID: 14565862
-
Synergism in survival to endotoxic shock in rats given microencapsulated CNI-1493 and antisense oligomers to NF-kappaB.J Microencapsul. 2010;27(4):372-6. doi: 10.3109/02652040903243437. J Microencapsul. 2010. PMID: 20515262
-
Prevention of lethality and suppression of proinflammatory cytokines in experimental septic shock by microencapsulated CNI-1493.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 1999 Oct;19(10):1125-33. doi: 10.1089/107999099313064. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 1999. PMID: 10547152
-
[The use of antisense oligonucleotides for modulation of cytokine gene expression].Vopr Med Khim. 1997 Sep-Oct;43(5):308-20. Vopr Med Khim. 1997. PMID: 9446321 Review. Russian.
-
Microencapsulation of protein drugs for drug delivery: strategy, preparation, and applications.J Control Release. 2014 Nov 10;193:324-40. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2014.09.003. Epub 2014 Sep 10. J Control Release. 2014. PMID: 25218676 Review.
Cited by
-
Novel treatment of neuroinflammation against low back pain by soluble fullerol nanoparticles.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013 Aug 1;38(17):1443-51. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0b013e31828fc6b7. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013. PMID: 23466506 Free PMC article.
-
Albumin nanostructures as advanced drug delivery systems.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2016 Nov;13(11):1609-1623. doi: 10.1080/17425247.2016.1193149. Epub 2016 Jun 3. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2016. PMID: 27216915 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Silylated precision particles for controlled release of proteins.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015 Mar 18;7(10):5756-67. doi: 10.1021/am508520z. Epub 2015 Mar 5. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015. PMID: 25742193 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akhavein N, Oettinger C, Gayakawad S, Addo R, Bejugam N, Bauer J, Pollock S, D'Souza M. Treatment of adjuvant arthritis using microencapsulated antisense to NF-κB oligonucleotides. J Microencapsulation. 2008;18:1–12. - PubMed
-
- Andreakos ET, Feldman M. Autoimmunity and cytokines: Pathogenesis and therapy. In: Thomsom AW, Lotze MT, editors. The cytokine handbook. 4th ed. II. San Diego, CA: Academic Press; 2003. pp. 1189–211.
-
- Bagby G, Plessala K, Wilson L, Thompson J, Nelson S. Divergent efficacy of antibody to tumor necrosis factor-α in intravascular and peritonitis models of sepsis. J Infect Dis. 1991;163:83–8. - PubMed
-
- Bender A, Schafer V, Steffan AM, Royer C, Kreuter J, Rubsamen-Waigmann H, von Briesen H. Inhibition of HIV in-vitro by antiviral drug-targeting using nanoparticles. Res Virol. 1994;145:215–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
