Sequence analysis of Epstein-Barr virus EBNA-2 gene coding amino acid 148-487 in nasopharyngeal and gastric carcinomas
- PMID: 22348267
- PMCID: PMC3312847
- DOI: 10.1186/1743-422X-9-49
Sequence analysis of Epstein-Barr virus EBNA-2 gene coding amino acid 148-487 in nasopharyngeal and gastric carcinomas
Abstract
Background: The Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) nuclear antigen 2 (EBNA-2) plays a key role in the B-cell growth transformation by initiating and maintaining the proliferation of infected B-cell upon EBV infection in vitro. Most studies about EBNA-2 have focused on its functions yet little is known for its intertypic polymorphisms.
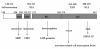
Results: Coding region for amino acid (aa) 148-487 of the EBNA-2 gene was sequenced in 25 EBV-associated gastric carcinomas (EBVaGCs), 56 nasopharyngeal carcinomas (NPCs) and 32 throat washings (TWs) from healthy donors in Northern China. Three variations (g48991t, c48998a, t49613a) were detected in all of the samples (113/113, 100%). EBNA-2 could be classified into four distinct subtypes: E2-A, E2-B, E2-C and E2-D based on the deletion status of three aa (294Q, 357K and 358G). Subtypes E2-A and E2-C were detected in 56/113 (49.6%), 38/113 (33.6%) samples, respectively. E2-A was observed more in EBVaGCs samples and subtype E2-D was only detected in the NPC samples. Variation analysis in EBNA-2 functional domains: the TAD residue (I438L) and the NLS residues (E476G, P484H and I486T) were only detected in NPC samples which located in the carboxyl terminus of EBNA-2 gene.
Conclusions: The subtypes E2-A and E2-C were the dominant genotypes of the EBNA-2 gene in Northern China. The subtype E2-D may be associated with the tumorigenesis of NPC. The NPC isolates were prone harbor to more mutations than the other two groups in the functional domains.
Figures

References
-
- Aitken C, Sengupta SK, Aedes C, Moss DJ, Sculley TB. Heterogeneity within the Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 gene in different strains of Epstein-Barr virus. J Gen Virol. 1994;75(Pt 1):95–100. - PubMed
-
- de-The G, Geser A, Day NE, Tukei PM, Williams EH, Beri DP, Smith PG, Dean AG, Bronkamm GW, Feorino P, Henle W. Epidemiological evidence for causal relationship between Epstein-Barr virus and Burkitt's lymphoma from Ugandan prospective study. Nature. 1978;274:756–761. doi: 10.1038/274756a0. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

