Regulation of Cu(I)/Ag(I) efflux genes in Escherichia coli by the sensor kinase CusS
- PMID: 22348296
- PMCID: PMC3319497
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2012.02529.x
Regulation of Cu(I)/Ag(I) efflux genes in Escherichia coli by the sensor kinase CusS
Abstract
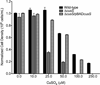
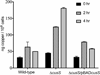
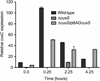
Two-component systems are widely used by bacteria to mediate adaptive responses to a variety of environmental stimuli. The CusR/CusS two-component system in Escherichia coli induces expression of genes involved in metal efflux under conditions of elevated Cu(I) and Ag(I) concentrations. As seen in most prototypical two-component systems, signal recognition and transmission is expected to occur by ligand binding in the periplasmic sensor domain of the histidine kinase CusS. Although discussed in the extant literature, little experimental evidence is available to establish the role of CusS in metal homeostasis. In this study, we show that the cusS gene is required for Cu(I) and Ag(I) resistance in E. coli and that CusS is linked to the expression of the cusCFBA genes. These results show a metal-dependent mechanism of CusS activation and suggest an absolute requirement for CusS in Cu(I)- and Ag(I)-dependent upregulation of cusCFBA expression in E. coli.
© 2012 Federation of European Microbiological Societies. Published by Blackwell Publishing Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Beswick PH, Hall GH, Hook AJ, Little K, McBrien DC, Lott KA. Copper toxicity: evidence for the conversion of cupric to cuprous copper in vivo under anaerobic conditions. Chem. Biol. Interact. 1976;14:347–356. - PubMed
-
- Bragg PD, Rainnie DJ. The effect of silver ions on the respiratory chain of Escherichia coli. Can. J. Microbiol. 1974;20:883–889. - PubMed
-
- Brown NL, Rouch DA, Lee BT. Copper resistance determinants in bacteria. Plasmid. 1992;27:41–51. - PubMed
-
- Cramp WA. The Toxic Action on Bacteria of Irradiated Solutions of Copper Compounds. Radiation Research. 1967;30:221–236. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

