Adrenomedullin, a neuropeptide with immunoregulatory properties induces semi-mature tolerogenic dendritic cells
- PMID: 22348691
- PMCID: PMC3403265
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2012.03577.x
Adrenomedullin, a neuropeptide with immunoregulatory properties induces semi-mature tolerogenic dendritic cells
Abstract
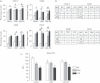
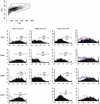
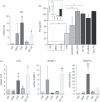
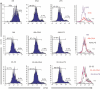
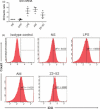
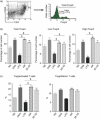
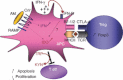
Dendritic cells (DC) play a pivotal role in tolerance. Adrenomedullin (AM), a neuropeptide with anti-apoptotic and anti-inflammatory effects, may decrease T helper type 1 effector cells and induce regulatory T (Treg) cells. The aim of this study was to evaluate AM effects on murine dendritic cell (DC) maturation and functions. Bone marrow-derived DC were produced and stimulated with CpG motifs, lipopolysaccharide or AM for 24 hr. Then, DC maturation and expression of AM and AM receptors were evaluated. Compared with lipopolysaccharide-stimulated or CpG-stimulated DC, AM-stimulated DC had lower levels of co-stimulatory molecule expression and pro-inflammatory cytokine release. The AM induced high levels of interferon-γ but not of interleukin-10. Importantly, AM inhibited lipopolysaccharide-induced maturation of DC. However, allogeneic T-cell stimulation and endocytic capacity of AM-stimulated DC were comparable to those of semi-mature and mature DC. Moreover, DC expressed AM and its receptors at a basal level, and AM receptor expression increased with DC maturation. The AM stimulation induced indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) expression, promoting Treg cell expansion. For the first time, we describe the DC maturation phenotype by a neuropeptide (AM). We have demonstrated that AM and its receptors are expressed in DC and that exogenous AM can modify the DC phenotype and functions and can induce a semi-mature DC phenotype with IDO expression. These results indicate close interactions among immune system regulation mechanisms and calcitonin-like peptides.
© 2012 The Authors. Immunology © 2012 Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Apoptotic cells induce dendritic cell-mediated suppression via interferon-gamma-induced IDO.Immunology. 2008 May;124(1):89-101. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2007.02743.x. Epub 2007 Dec 7. Immunology. 2008. PMID: 18067553 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of human auto- and alloreactive T cells by indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO)-producing dendritic cells: too much ado about IDO?Blood. 2005 Mar 15;105(6):2480-6. doi: 10.1182/blood-2004-06-2103. Epub 2004 Nov 30. Blood. 2005. PMID: 15572592
-
Allostimulatory activity of bone marrow-derived plasmacytoid dendritic cells is independent of indoleamine dioxygenase but regulated by inducible costimulator ligand expression.Hum Immunol. 2009 May;70(5):313-20. doi: 10.1016/j.humimm.2009.01.021. Epub 2009 Feb 3. Hum Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19208362 Free PMC article.
-
Use of rapamycin in the induction of tolerogenic dendritic cells.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2009;(188):215-32. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-71029-5_10. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19031028 Review.
-
The Dendritic Cell Dilemma in the Skin: Between Tolerance and Immunity.Front Immunol. 2022 Jun 28;13:929000. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.929000. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35837386 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
An RNA vaccine against adrenomedullin reduces angiogenesis and tumor burden in a syngeneic metastatic melanoma mouse model.Front Immunol. 2025 Jun 5;16:1604156. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1604156. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40539045 Free PMC article.
-
Adrenomedullin Expression Characterizes Leukemia Stem Cells and Associates With an Inflammatory Signature in Acute Myeloid Leukemia.Front Oncol. 2021 Jun 2;11:684396. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.684396. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34150648 Free PMC article.
-
Sex differences in the tumor promoting effects of tobacco smoke in a cRaf transgenic lung cancer disease model.Arch Toxicol. 2024 Mar;98(3):957-983. doi: 10.1007/s00204-023-03671-5. Epub 2024 Jan 21. Arch Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 38245882 Free PMC article.
-
Leukemia-associated activating mutation of Flt3 expands dendritic cells and alters T cell responses.J Exp Med. 2016 Mar 7;213(3):415-31. doi: 10.1084/jem.20150642. Epub 2016 Feb 22. J Exp Med. 2016. PMID: 26903243 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the toxicity of iron-ion irradiation in murine bone marrow dendritic cells via increasing the expression of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1.Toxicol Res (Camb). 2017 Sep 25;6(6):958-968. doi: 10.1039/c7tx00194k. eCollection 2017 Nov 1. Toxicol Res (Camb). 2017. PMID: 30090556 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liu K, Nussenzweig MC. Origin and development of dendritic cells. Immunol Rev. 2010;234:45–54. - PubMed
-
- Coquerelle C, Moser M. DC subsets in positive and negative regulation of immunity. Immunol Rev. 2010;234:317–34. - PubMed
-
- Charbonnier LM, van Duivenvoorde LM, Apparailly F, et al. Immature dendritic cells suppress collagen-induced arthritis by in vivo expansion of CD49b+ regulatory T cells. J Immunol. 2006;177:3806–13. - PubMed
-
- van Duivenvoorde LM, Louis-Plence P, Apparailly F, van der Voort EI, Huizinga TW, Jorgensen C, Toes RE. Antigen-specific immunomodulation of collagen-induced arthritis with tumor necrosis factor-stimulated dendritic cells. Arthritis Rheum. 2004;50:3354–64. - PubMed
-
- Hill M, Tanguy-Royer S, Royer P, et al. IDO expands human CD4+ CD25high regulatory T cells by promoting maturation of LPS-treated dendritic cells. Eur J Immunol. 2007;37:3054–62. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

