Lactobacillus acidophilus and Lactobacillus reuteri modulate cytokine responses in gnotobiotic pigs infected with human rotavirus
- PMID: 22348907
- PMCID: PMC3304463
- DOI: 10.3920/BM2011.0041
Lactobacillus acidophilus and Lactobacillus reuteri modulate cytokine responses in gnotobiotic pigs infected with human rotavirus
Abstract
Probiotic lactic acid bacteria (LAB) have been shown to alleviate inflammation, enhance the immunogenicity of rotavirus vaccines, or reduce the severity of rotavirus diarrhoea. Although the mechanisms are not clear, the differential Th1/Th2/Th3-driving capacities and modulating effects on cytokine production of different LAB strains may be the key. Our goal was to delineate the influence of combining two probiotic strains of Lactobacillus acidophilus and Lactobacillus reuteri on the development of cytokine responses in neonatal gnotobiotic pigs infected with human rotavirus (HRV). We demonstrated that HRV alone, or HRV plus LAB, but not LAB alone, initiated serum cytokine responses, as indicated by significantly higher concentrations of IFN-α, IFN-γ, IL-12, and IL-10 at postinoculation day (PID) 2 in the HRV only and LAB+HRV+ pigs compared to LAB only and LAB-HRV- pigs. Peak cytokine responses coincided with the peak of HRV replication. LAB further enhanced the Th1 and Th2 cytokine responses to HRV infection as indicated by significantly higher concentrations of IL-12, IFN-γ, IL-4 and IL-10 in the LAB+HRV+ pigs compared to the LAB-HRV+ pigs. The LAB+HRV+ pigs maintained relatively constant concentrations of TGF-β compared to the HRV only group which had a significant increase at PID 2 and decrease at PID 7, suggesting a regulatory role of LAB in maintaining gut homeostasis. At PID 28, cytokine secreting cell (CSC) responses, measured by ELISpot, showed increased Th1 (IL-12, IFN-γ) CSC numbers in the LAB+HRV+ and LAB-HRV+ groups compared to LAB only and LAB-HRV- pigs, with significantly increased IL-12 CSCs in spleen and PBMCs and IFN-γ CSCs in spleen of the LAB+HRV+ group. Thus, HRV infection alone, but not LAB alone was effective in inducing cytokine responses but LAB significantly enhanced both Th1 and Th2 cytokines in HRV-infected pigs. LAB may also help to maintain immunological homeostasis during HRV infection by regulating TGF-β production.
Figures
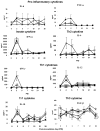
 - LAB-HRV−
- LAB-HRV−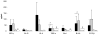
 - LAB-HRV+;
- LAB-HRV+;
 - LAB+HRV−; □ - LAB-HRV−
- LAB+HRV−; □ - LAB-HRV−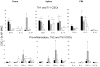
 - LAB-HRV+;
- LAB-HRV+;
 - LAB+HRV−; □ - LAB-HRV−
- LAB+HRV−; □ - LAB-HRV−References
-
- Azevedo MS, Yuan L, Iosef C, Chang KO, Kim Y, Nguyen TV, Saif LJ. Magnitude of serum and intestinal antibody responses induced by sequential replicating and nonreplicating rotavirus vaccines in gnotobiotic pigs and correlation with protection. Clinical & Diagnostic Laboratory Immunology. 2004;11:12–20. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Boirivant M, Strober W. The mechanism of action of probiotics. Current Opinion in Gastroenterology. 2007;23:679–692. - PubMed
-
- Christensen HR, Frokiar H, Pestka JJ. Lactobacilli Differentially Modulate Expression of Cytokines and Maturation Surface Markers in Murine Dendritic Cells. Journal of Immunology. 2002;168:171–178. - PubMed
-
- Fink LN, Zeuthen LH, Christensen HR, Morandi B, Frokiaer H, Ferlazzo G. Distinct gut-derived lactic acid bacteria elicit divergent dendritic cell-mediated NK cell responses. International Immunology. 2007;19:1319–1327. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

