Making alternative splicing decisions during epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT)
- PMID: 22349259
- PMCID: PMC11115103
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-012-0931-7
Making alternative splicing decisions during epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT)
Abstract
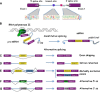
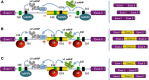
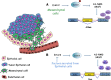
Alternative splicing generates multiple mRNAs from a single transcript and is a major contributor to proteomic diversity and to the control of gene expression in complex organisms. Not surprisingly, this post-transcriptional event is tightly regulated in different tissues and developmental stages. An increasing body of evidences supports a causative role of aberrant alternative splicing in cancer. However, very little is known about its impact on cellular processes crucially involved in tumor progression. The aim of this review is to discuss the link between alternative splicing and the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT), one of the major routes by which cancer cells acquire invasive capabilities and become metastatic. We begin with a brief overview of alternative splicing. Next, we discuss alternative splicing factors that regulate EMT. Finally, we provide examples of target genes presenting alternative splicing changes that contribute to the morphological conversions in the EMT process.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

