Overexpression of HIF-1α transgene in the renal medulla attenuated salt sensitive hypertension in Dahl S rats
- PMID: 22349312
- PMCID: PMC3402054
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2012.02.002
Overexpression of HIF-1α transgene in the renal medulla attenuated salt sensitive hypertension in Dahl S rats
Abstract
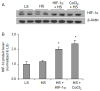
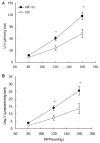
Hypoxia inducible factor (HIF)-1α-mediated gene activation in the renal medulla in response to high salt intake plays an important role in the control of salt sensitivity of blood pressure. High salt-induced activation of HIF-1α in the renal medulla is blunted in Dahl S rats. The present study determined whether the impairment of the renal medullary HIF-1α pathway was responsible for salt sensitive hypertension in Dahl S rats. Renal medullary HIF-1α levels were induced by either transfection of HIF-1α expression plasmid or chronic infusion of CoCl₂ into the renal medulla, which was accompanied by increased expressions of anti-hypertensive genes, cyclooxygenase-2 and heme oxygenase-1. Overexpression of HIF-1α transgenes in the renal medulla enhanced the pressure natriuresis, promoted the sodium excretion and reduced sodium retention after salt overload. As a result, hypertension induced by 2-week high salt was significantly attenuated in rats treated with HIF-1α plasmid or CoCl₂. These results suggest that an abnormal HIF-1α in the renal medulla may represent a novel mechanism mediating salt-sensitive hypertension in Dahl S rats and that induction of HIF-1α levels in the renal medulla could be a therapeutic approach for the treatment of salt-sensitive hypertension.
© 2012 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures




Similar articles
-
Silencing of HIF prolyl-hydroxylase 2 gene in the renal medulla attenuates salt-sensitive hypertension in Dahl S rats.Am J Hypertens. 2014 Jan;27(1):107-13. doi: 10.1093/ajh/hpt207. Epub 2013 Nov 4. Am J Hypertens. 2014. PMID: 24190904 Free PMC article.
-
Salt-sensitive hypertension induced by decoy of transcription factor hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha in the renal medulla.Circ Res. 2008 May 9;102(9):1101-8. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.107.169201. Epub 2008 Mar 20. Circ Res. 2008. PMID: 18356541 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of HIF prolyl-hydoxylase-2 transgene in the renal medulla induced a salt sensitive hypertension.J Cell Mol Med. 2012 Nov;16(11):2701-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2012.01590.x. J Cell Mol Med. 2012. PMID: 22686466 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation and function of renal medullary cyclooxygenase-2 during high salt loading.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2017 Jan 1;22(1):128-136. doi: 10.2741/4476. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2017. PMID: 27814606 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Animal models of hypertension: The status of nitric oxide and oxidative stress and the role of the renal medulla.Nitric Oxide. 2022 Aug 1;125-126:40-46. doi: 10.1016/j.niox.2022.06.003. Epub 2022 Jun 11. Nitric Oxide. 2022. PMID: 35700961 Review.
Cited by
-
Hypoxia-inducible factors and essential hypertension: narrative review of experimental and clinical data.Pharmacol Rep. 2023 Aug;75(4):861-875. doi: 10.1007/s43440-023-00497-x. Epub 2023 May 21. Pharmacol Rep. 2023. PMID: 37210694 Review.
-
Fumarate and its downstream signalling pathways in the cardiorenal system: Recent insights and novel expositions in the etiology of hypertension.Eur J Pharmacol. 2023 Dec 15;961:176186. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2023.176186. Epub 2023 Nov 8. Eur J Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37944846 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Infusion of Valproic Acid Into the Renal Medulla Activates Stem Cell Population and Attenuates Salt-Sensitive Hypertension in Dahl S Rats.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;42(3):1264-1273. doi: 10.1159/000478955. Epub 2017 Jul 11. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28693025 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of echinomycin on endothelin-2 expression and ovulation in immature rats primed with gonadotropins.Exp Mol Med. 2012 Oct 31;44(10):615-21. doi: 10.3858/emm.2012.44.10.070. Exp Mol Med. 2012. PMID: 22874467 Free PMC article.
-
Detrimental role of sphingosine kinase 1 in kidney damage in DOCA-salt hypertensive model: evidence from knockout mice.BMC Nephrol. 2020 May 11;21(1):173. doi: 10.1186/s12882-020-01815-8. BMC Nephrol. 2020. PMID: 32393187 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Weinberger MH, Miller JZ, Luft FC, Grim CE, Fineberg NS. Definitions and characteristics of sodium sensitivity and blood pressure resistance. Hypertension. 1986;8:II127–134. - PubMed
-
- Chrysant GS, Bakir S, Oparil S. Dietary salt reduction in hypertension--what is the evidence and why is it still controversial? Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 1999;42:23–38. - PubMed
-
- Campese V. Salt sensitivity in hypertension. Renal and cardiovascular implications [clinical conference] Hypertension. 1994;23:531–550. - PubMed
-
- Weinberger MH, Fineberg NS, Fineberg SE, Weinberger M. Salt Sensitivity, Pulse Pressure, and Death in Normal and Hypertensive Humans. Hypertension. 2001;37:429–432. - PubMed
-
- Cowley AWMD, Jr, Lu S, Roman RJ. The renal medulla and hypertension. Hypertension. 1995;25:663–673. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

