Phosphoproteomic differences in major depressive disorder postmortem brains indicate effects on synaptic function
- PMID: 22350622
- PMCID: PMC3491199
- DOI: 10.1007/s00406-012-0301-3
Phosphoproteomic differences in major depressive disorder postmortem brains indicate effects on synaptic function
Abstract
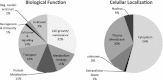
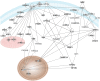
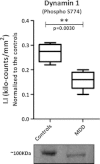
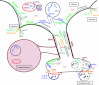
There is still a lack in the molecular comprehension of major depressive disorder (MDD) although this condition affects approximately 10% of the world population. Protein phosphorylation is a posttranslational modification that regulates approximately one-third of the human proteins involved in a range of cellular and biological processes such as cellular signaling. Whereas phosphoproteome studies have been carried out extensively in cancer research, few such investigations have been carried out in studies of psychiatric disorders. Here, we present a comparative phosphoproteome analysis of postmortem dorsolateral prefrontal cortex tissues from 24 MDD patients and 12 control donors. Tissue extracts were analyzed using liquid chromatography mass spectrometry in a data-independent manner (LC-MS(E)). Our analyses resulted in the identification of 5,195 phosphopeptides, corresponding to 802 non-redundant proteins. Ninety of these proteins showed differential levels of phosphorylation in tissues from MDD subjects compared to controls, being 20 differentially phosphorylated in at least 2 peptides. The majority of these phosphorylated proteins were associated with synaptic transmission and cellular architecture not only pointing out potential biomarker candidates but mainly shedding light to the comprehension of MDD pathobiology.
Figures
References
-
- Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J R Stat Soc. 1995;57:289–300.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

