Measuring rates of ubiquitin chain formation as a functional readout of ligase activity
- PMID: 22350887
- PMCID: PMC3579653
- DOI: 10.1007/978-1-61779-474-2_14
Measuring rates of ubiquitin chain formation as a functional readout of ligase activity
Abstract
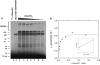
Specificity within the pathways of ubiquitin conjugation are defined by protein-binding affinities among the components. Enzyme kinetics provides a facile high-resolution experimental approach for quantitating such protein-binding affinities and yields additional mechanistic insights into the transition state of the enzyme-catalyzed reaction. Most ubiquitin ligases form free polyubiquitin chains at a slow rate in the absence of their cognate target protein as a normal step in their overall catalytic cycle. Rates of polyubiquitin chain formation can, therefore, be used as a reporter function kinetically to characterize binding interactions within the ligation pathway. We describe experimental approaches for: (1) precisely quantitating functional E1 and E2 concentrations by their stoichiometric formation of (125)I-ubiquitin thiolester; (2) semiquantitative screens to define the cognate E2(s) for ubiquitin ligases based on their ability to support polyubiquitin chain formation; (3) initial rate studies to quantify K (m) and k (cat) as a measure of the ability of specific E2-ubiquitin thiolester substrates to support ligase-catalyzed polyubiquitin chain formation; and (4) an isopeptidase T-based technique for distinguishing between free and conjugated polyubiquitin chains formed in the functional assays. These kinetic methods provide mechanistic insights that are otherwise inaccessible by other experimental approaches and yield a precision in characterizing protein interactions that exceeds that of other techniques.
Figures
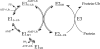


Similar articles
-
Tripartite motif ligases catalyze polyubiquitin chain formation through a cooperative allosteric mechanism.J Biol Chem. 2013 Mar 22;288(12):8209-8221. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.451567. Epub 2013 Feb 13. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23408431 Free PMC article.
-
E6AP/UBE3A ubiquitin ligase harbors two E2~ubiquitin binding sites.J Biol Chem. 2013 Apr 12;288(15):10349-60. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.458059. Epub 2013 Feb 25. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23439649 Free PMC article.
-
Orchestra for assembly and fate of polyubiquitin chains.Essays Biochem. 2005;41:1-14. doi: 10.1042/EB0410001. Essays Biochem. 2005. PMID: 16250894 Review.
-
Analysis of ubiquitin E3 ligase activity using selective polyubiquitin binding proteins.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Nov;1823(11):2094-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2012.06.013. Epub 2012 Jun 18. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012. PMID: 22721718 Free PMC article.
-
Multiubiquitylation by E4 enzymes: 'one size' doesn't fit all.Trends Biochem Sci. 2005 Apr;30(4):183-7. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2005.02.004. Trends Biochem Sci. 2005. PMID: 15817394 Review.
Cited by
-
Tripartite motif ligases catalyze polyubiquitin chain formation through a cooperative allosteric mechanism.J Biol Chem. 2013 Mar 22;288(12):8209-8221. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.451567. Epub 2013 Feb 13. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23408431 Free PMC article.
-
The active form of E6-associated protein (E6AP)/UBE3A ubiquitin ligase is an oligomer.J Biol Chem. 2014 Jan 10;289(2):1033-48. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.517805. Epub 2013 Nov 22. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24273172 Free PMC article.
-
E6AP/UBE3A ubiquitin ligase harbors two E2~ubiquitin binding sites.J Biol Chem. 2013 Apr 12;288(15):10349-60. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.458059. Epub 2013 Feb 25. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23439649 Free PMC article.
-
Oligomerization of the HECT ubiquitin ligase NEDD4-2/NEDD4L is essential for polyubiquitin chain assembly.J Biol Chem. 2018 Nov 23;293(47):18192-18206. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.003716. Epub 2018 Oct 4. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 30287686 Free PMC article.
-
UbFluor: A Fluorescent Thioester to Monitor HECT E3 Ligase Catalysis.Curr Protoc Chem Biol. 2017 Mar 2;9(1):11-37. doi: 10.1002/cpch.17. Curr Protoc Chem Biol. 2017. PMID: 28253433 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Haas AL, Siepmann TJ. Pathways of ubiquitin conjugation. Faseb J. 1997;11:1257–1268. - PubMed
-
- Haas AL, Warms JV, Hershko A, Rose IA. Ubiquitin-activating enzyme. Mechanism and role in protein-ubiquitin conjugation. J Biol Chem. 1982;257:2543–2548. - PubMed
-
- Haas AL, Rose IA. The mechanism of ubiquitin activating enzyme. A kinetic and equilibrium analysis. J Biol Chem. 1982;257:10329–10337. - PubMed
-
- Streich FC, Haas AL. Activation of ubiquitin and ubiquitin-like proteins. Subcell. Biochem. 2010;54:1–16. - PubMed
-
- Pickart CM. Mechanism underlying ubiquitination. Annu Rev Biochem. 2001;70:503–533. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

