MicroRNA dysregulation in cancer: diagnostics, monitoring and therapeutics. A comprehensive review
- PMID: 22351564
- PMCID: PMC3376845
- DOI: 10.1002/emmm.201100209
MicroRNA dysregulation in cancer: diagnostics, monitoring and therapeutics. A comprehensive review
Erratum in
-
MicroRNA dysregulation in cancer: diagnostics, monitoring and therapeutics. A comprehensive review.EMBO Mol Med. 2017 Jun;9(6):852. doi: 10.15252/emmm.201707779. EMBO Mol Med. 2017. PMID: 28572088 Free PMC article.
Abstract
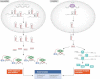
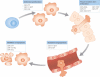
Early studies have shown how aberrantly expressed microRNAs are a hallmark of several diseases like cancer. MicroRNA expression profiling was shown to be associated with tumour development, progression and response to therapy, suggesting their possible use as diagnostic, prognostic and predictive biomarkers. Moreover, based on the increasing number of studies demonstrating that microRNAs can function as potential oncogenes or oncosuppressor genes, with the goal to improve disease response and increase cure rates, miRNA-based anticancer therapies have recently been exploited, either alone or in combination with current targeted therapies. The advantage of using microRNA approaches is based on its ability to concurrently target multiple effectors of pathways involved in cell differentiation, proliferation and survival. Here, we review our current knowledge about the involvement of microRNAs in cancer, and their potential as diagnostic, prognostic and therapeutic tools.
Copyright © 2012 EMBO Molecular Medicine.
Figures
References
-
- Asangani IA, Rasheed SA, Nikolova DA, Leupold JH, Colburn NH, Post S, Allgayer H. MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) post-transcriptionally downregulates tumor suppressor Pdcd4 and stimulates invasion, intravasation and metastasis in colorectal cancer. Oncogene. 2008;27:2128–2136. - PubMed
-
- Beitzinger M, Meister G. Preview. MicroRNAs: from decay to decoy. Cell. 2010;140:612–614. - PubMed
-
- Benetti R, Gonzalo S, Jaco I, Munoz P, Gonzalez S, Schoeftner S, Murchison E, Andl T, Chen T, Klatt P, et al. A mammalian microRNA cluster controls DNA methylation and telomere recombination via Rbl2-dependent regulation of DNA methyltransferases. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2008;15:268–279. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources