Implications of plasma protein binding for pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of the γ-secretase inhibitor RO4929097
- PMID: 22351688
- PMCID: PMC3856649
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-2684
Implications of plasma protein binding for pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of the γ-secretase inhibitor RO4929097
Abstract
Purpose: Understanding of plasma protein binding will provide mechanistic insights into drug interactions or unusual pharmacokinetic properties. This study investigated RO4929097 binding in plasma and its implications for the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of this compound.
Experimental design: RO4929097 binding to plasma proteins was determined using a validated equilibrium dialysis method. Pharmacokinetics of total and unbound RO4929097 was evaluated in eight patients with breast cancer receiving RO4929097 alone and in combination with the Hedgehog inhibitor GDC-0449. The impact of protein binding on RO4929097 pharmacodynamics was assessed using an in vitro Notch cellular assay.
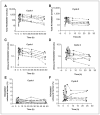
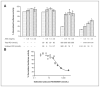
Results: RO4929097 was extensively bound in human plasma, with the total binding constant of 1.0 × 10(6) and 1.8 × 10(4) L/mol for α1-acid glycoprotein (AAG) and albumin, respectively. GDC-0449 competitively inhibited RO4929097 binding to AAG. In patients, RO4929097 fraction unbound (Fu) exhibited large intra- and interindividual variability; GDC-0449 increased RO4929097 Fu by an average of 3.7-fold. Concomitant GDC-0449 significantly decreased total (but not unbound) RO4929097 exposure. RO4929097 Fu was strongly correlated with the total drug exposure. Binding to AAG abrogated RO4929097 in vitro Notch-inhibitory activity.
Conclusions: RO4929097 is highly bound in human plasma with high affinity to AAG. Changes in plasma protein binding caused by concomitant drug (e.g., GDC-0449) or disease states (e.g., ↑AAG level in cancer) can alter total (but not unbound) RO4929097 exposure. Unbound RO4929097 is pharmacologically active. Monitoring of unbound RO4929097 plasma concentration is recommended to avoid misleading conclusions on the basis of the total drug levels.
©2012 AACR.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Pharmacokinetics of hedgehog pathway inhibitor vismodegib (GDC-0449) in patients with locally advanced or metastatic solid tumors: the role of alpha-1-acid glycoprotein binding.Clin Cancer Res. 2011 Apr 15;17(8):2512-20. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-2736. Epub 2011 Feb 7. Clin Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 21300760 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Validation and implementation of a liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry assay for quantitation of the total and unbound RO4929097, a γ-secretase inhibitor targeting Notch signaling, in human plasma.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2011 Jun 1;879(19):1537-43. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2011.03.045. Epub 2011 Mar 31. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2011. PMID: 21497565 Free PMC article.
-
A phase I study of an oral selective gamma secretase (GS) inhibitor RO4929097 in combination with neoadjuvant paclitaxel and carboplatin in triple negative breast cancer.Invest New Drugs. 2020 Oct;38(5):1400-1410. doi: 10.1007/s10637-020-00895-5. Epub 2020 Jan 17. Invest New Drugs. 2020. PMID: 31953695 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Protein binding in antiretroviral therapies.AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2003 Sep;19(9):825-35. doi: 10.1089/088922203769232629. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2003. PMID: 14585213 Review.
-
Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Considerations for Drugs Binding to Alpha-1-Acid Glycoprotein.Pharm Res. 2018 Dec 28;36(2):30. doi: 10.1007/s11095-018-2551-x. Pharm Res. 2018. PMID: 30593605 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Phase Ib Dose Escalation Trial of RO4929097 (a γ-secretase inhibitor) in Combination with Exemestane in Patients with ER + Metastatic Breast Cancer (MBC).Clin Breast Cancer. 2022 Feb;22(2):103-114. doi: 10.1016/j.clbc.2021.10.013. Epub 2021 Oct 28. Clin Breast Cancer. 2022. PMID: 34903452 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A phase I study of the combination of ro4929097 and cediranib in patients with advanced solid tumours (PJC-004/NCI 8503).Br J Cancer. 2013 Aug 20;109(4):943-9. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2013.380. Epub 2013 Jul 18. Br J Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23868004 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A phase I study of the oral gamma secretase inhibitor R04929097 in combination with gemcitabine in patients with advanced solid tumors (PHL-078/CTEP 8575).Invest New Drugs. 2014 Apr;32(2):243-9. doi: 10.1007/s10637-013-9965-4. Epub 2013 May 5. Invest New Drugs. 2014. PMID: 23645447 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Consideration of the Unbound Drug Concentration in Enzyme Kinetics.Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2342:113-145. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1554-6_5. Methods Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 34272693
-
Addressing the Accuracy of Plasma Protein Binding Measurement for Highly Bound Compounds Using the Dilution Method.AAPS J. 2022 Dec 5;25(1):7. doi: 10.1208/s12248-022-00774-2. AAPS J. 2022. PMID: 36471200
References
-
- Fortini ME. Notch signaling: the core pathway and its posttranslational regulation. Dev Cell. 2009;16:633–47. - PubMed
-
- Baldi A, De Falco M, De Luca L, Cottone G, Paggi MG, Nickoloff BJ, et al. Characterization of tissue specific expression of Notch-1 in human tissues. Biol Cell. 2004;96:303–11. - PubMed
-
- Shih Ie M, Wang TL. Notch signaling, gamma-secretase inhibitors, and cancer therapy. Cancer Res. 2007;67:1879–82. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

