RAF265 inhibits the growth of advanced human melanoma tumors
- PMID: 22351689
- PMCID: PMC3724517
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-1122
RAF265 inhibits the growth of advanced human melanoma tumors
Erratum in
- Clin Cancer Res. 2012 Aug 15;18(16):4475
Abstract
Purpose: The purpose of this preclinical study was to determine the effectiveness of RAF265, a multikinase inhibitor, for treatment of human metastatic melanoma and to characterize traits associated with drug response.
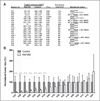
Experimental design: Advanced metastatic melanoma tumors from 34 patients were orthotopically implanted to nude mice. Tumors that grew in mice (17 of 34) were evaluated for response to RAF265 (40 mg/kg, every day) over 30 days. The relation between patient characteristics, gene mutation profile, global gene expression profile, and RAF265 effects on tumor growth, mitogen-activated protein/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (MEK)/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) phosphorylation, proliferation, and apoptosis markers was evaluated.
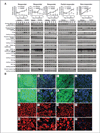
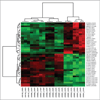
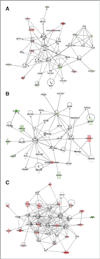
Results: Nine of the 17 tumors that successfully implanted (53%) were mutant BRAF (BRAF(V600E/K)), whereas eight of 17 (47%) tumors were BRAF wild type (BRAF(WT)). Tumor implants from 7 of 17 patients (41%) responded to RAF265 treatment with more than 50% reduction in tumor growth. Five of the 7 (71%) responders were BRAF(WT), of which 1 carried c-KIT(L576P) and another N-RAS(Q61R) mutation, while only 2 (29%) of the responding tumors were BRAF(V600E/K). Gene expression microarray data from nonimplanted tumors revealed that responders exhibited enriched expression of genes involved in cell growth, proliferation, development, cell signaling, gene expression, and cancer pathways. Although response to RAF265 did not correlate with pERK1/2 reduction, RAF265 responders did exhibit reduced pMEK1, reduced proliferation based upon reduced Ki-67, cyclin D1 and polo-like kinase1 levels, and induction of the apoptosis mediator BCL2-like 11.
Conclusions: Orthotopic implants of patient tumors in mice may predict prognosis and treatment response for melanoma patients. A subpopulation of human melanoma tumors responds to RAF265 and can be characterized by gene mutation and gene expression profiles.
©2012 AACR.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A first-in-human phase I, multicenter, open-label, dose-escalation study of the oral RAF/VEGFR-2 inhibitor (RAF265) in locally advanced or metastatic melanoma independent from BRAF mutation status.Cancer Med. 2017 Aug;6(8):1904-1914. doi: 10.1002/cam4.1140. Epub 2017 Jul 18. Cancer Med. 2017. PMID: 28719152 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Use of DNA microarray and small animal positron emission tomography in preclinical drug evaluation of RAF265, a novel B-Raf/VEGFR-2 inhibitor.Neoplasia. 2011 Mar;13(3):266-75. doi: 10.1593/neo.101466. Neoplasia. 2011. PMID: 21390189 Free PMC article.
-
Protein kinase D3 sensitizes RAF inhibitor RAF265 in melanoma cells by preventing reactivation of MAPK signaling.Cancer Res. 2011 Jun 15;71(12):4280-91. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-3761. Epub 2011 Apr 28. Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 21527556
-
BRAF signaling and targeted therapies in melanoma.Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2009 Jun;23(3):529-45, ix. doi: 10.1016/j.hoc.2009.04.001. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2009. PMID: 19464601 Review.
-
BRAF-Driven Pancreatic Cancer: Prevalence, Molecular Features, and Therapeutic Opportunities.Mol Cancer Res. 2023 Apr 1;21(4):293-300. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-22-0626. Mol Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 36534729 Review.
Cited by
-
Advances in personalized targeted treatment of metastatic melanoma and non-invasive tumor monitoring.Front Oncol. 2013 Mar 19;3:54. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2013.00054. eCollection 2013. Front Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23515890 Free PMC article.
-
NRAS mutant melanoma: biological behavior and future strategies for therapeutic management.Oncogene. 2013 Jun 20;32(25):3009-18. doi: 10.1038/onc.2012.453. Epub 2012 Oct 15. Oncogene. 2013. PMID: 23069660 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A systematic study on drug-response associated genes using baseline gene expressions of the Cancer Cell Line Encyclopedia.Sci Rep. 2016 Mar 10;6:22811. doi: 10.1038/srep22811. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26960563 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting aurora kinases limits tumour growth through DNA damage-mediated senescence and blockade of NF-κB impairs this drug-induced senescence.EMBO Mol Med. 2013 Jan;5(1):149-66. doi: 10.1002/emmm.201201378. Epub 2012 Nov 25. EMBO Mol Med. 2013. PMID: 23180582 Free PMC article.
-
Small Molecules Antagonise the MIA-Fibronectin Interaction in Malignant Melanoma.Sci Rep. 2016 May 6;6:25119. doi: 10.1038/srep25119. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27151361 Free PMC article.
References
-
- National Cancer Institute N, DHHS. Cancer trends progress report-2009/2010 update. 2010.
-
- Natarajan N, Telang S, Miller D, Chesney J. Novel immunotherapeutic agents and small molecule antagonists of signalling kinases for the treatment of metastatic melanoma. Drugs. 2011;71:1233–1250. - PubMed
-
- Vogelstein B, Kinzler KW. Cancer genes and the pathways they control. Nat Med. 2004;10:789–799. - PubMed
-
- Janne PA, Gray N, Settleman J. Factors underlying sensitivity of cancers to small-molecule kinase inhibitors. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2009;8:709–723. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
- IK6 BX005225/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- 5P30CA068485/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K24 CA097588/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 2 UL1 TR000445-06/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX000196/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- P30 CA068485/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA116021/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K12 GM068543/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- CA116021/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA119925/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K12 CA090625/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K12-CA090625/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 FD002333/FD/FDA HHS/United States
- T32 119925/PHS HHS/United States
- T32HL07751/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

