Responsiveness of intrinsic subtypes to adjuvant anthracycline substitution in the NCIC.CTG MA.5 randomized trial
- PMID: 22351696
- PMCID: PMC3743660
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-2956
Responsiveness of intrinsic subtypes to adjuvant anthracycline substitution in the NCIC.CTG MA.5 randomized trial
Abstract
Purpose: Recent studies suggest that intrinsic breast cancer subtypes may differ in their responsiveness to specific chemotherapy regimens. We examined this hypothesis on NCIC.CTG MA.5, a clinical trial randomizing premenopausal women with node-positive breast cancer to adjuvant CMF (cyclophosphamide-methotrexate-fluorouracil) versus CEF (cyclophosphamide-epirubicin-fluorouracil) chemotherapy.
Experimental design: Intrinsic subtype was determined for 476 tumors using the quantitative reverse transcriptase PCR PAM50 gene expression test. Luminal A, luminal B, HER2-enriched (HER2-E), and basal-like subtypes were correlated with relapse-free survival (RFS) and overall survival (OS), estimated using Kaplan-Meier plots and log-rank testing. Multivariable Cox regression analyses determined significance of interaction between treatment and intrinsic subtypes.
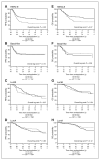
Results: Intrinsic subtypes were associated with RFS (P = 0.0005) and OS (P < 0.0001) on the combined cohort. The HER2-E showed the greatest benefit from CEF versus CMF, with absolute 5-year RFS and OS differences exceeding 20%, whereas there was a less than 2% difference for non-HER2-E tumors (interaction test P = 0.03 for RFS and 0.03 for OS). Within clinically defined Her2(+) tumors, 79% (72 of 91) were classified as the HER2-E subtype by gene expression and this subset was strongly associated with better response to CEF versus CMF (62% vs. 22%, P = 0.0006). There was no significant difference in benefit between CEF and CMF in basal-like tumors [n = 94; HR, 1.1; 95% confidence interval (CI), 0.6-2.1 for RFS and HR, 1.3; 95% CI, 0.7-2.5 for OS].
Conclusion: HER2-E strongly predicted anthracycline sensitivity. The chemotherapy-sensitive basal-like tumors showed no added benefit for CEF over CMF, suggesting that nonanthracycline regimens may be adequate in this subtype although further investigation is required.
©2012 AACR.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Topoisomerase II alpha protein and responsiveness of breast cancer to adjuvant chemotherapy with CEF compared to CMF in the NCIC CTG randomized MA.5 adjuvant trial.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2011 Jul;128(2):401-9. doi: 10.1007/s10549-011-1511-5. Epub 2011 Apr 26. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2011. PMID: 21519837 Clinical Trial.
-
TIMP-1 in combination with HER2 and TOP2A for prediction of benefit from adjuvant anthracyclines in high-risk breast cancer patients.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012 Feb;132(1):225-34. doi: 10.1007/s10549-011-1896-1. Epub 2011 Dec 9. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012. PMID: 22160637 Clinical Trial.
-
Topoisomerase II alpha and responsiveness of breast cancer to adjuvant chemotherapy.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2009 May 6;101(9):644-50. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djp067. Epub 2009 Apr 28. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2009. PMID: 19401546 Free PMC article.
-
Adjuvant chemotherapy in early breast cancer.Dan Med J. 2016 May;63(5):B5222. Dan Med J. 2016. PMID: 27127018 Review.
-
Selection of adjuvant chemotherapy for treatment of node-positive breast cancer.Lancet Oncol. 2005 Nov;6(11):886-98. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(05)70424-1. Lancet Oncol. 2005. PMID: 16257797 Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical target sequencing for precision medicine of breast cancer.Int J Clin Oncol. 2019 Feb;24(2):131-140. doi: 10.1007/s10147-018-1373-5. Epub 2019 Jan 2. Int J Clin Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30604156 Review.
-
Identification of a five-lncRNA signature for predicting the risk of tumor recurrence in patients with breast cancer.Int J Cancer. 2018 Nov 1;143(9):2150-2160. doi: 10.1002/ijc.31573. Epub 2018 Jul 28. Int J Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29707762 Free PMC article.
-
DNA Methylation Signatures Predicting Bevacizumab Efficacy in Metastatic Breast Cancer.Theranostics. 2018 Mar 11;8(8):2278-2288. doi: 10.7150/thno.23544. eCollection 2018. Theranostics. 2018. PMID: 29721079 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of baseline BMI and weight change in CCTG adjuvant breast cancer trials.Ann Oncol. 2017 Jul 1;28(7):1560-1568. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdx152. Ann Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28379421 Free PMC article.
-
Prosigna Risk of Recurrence score and intrinsic subtypes are associated with adjuvant anthracycline chemotherapy benefit in high-risk breast cancer.NPJ Breast Cancer. 2025 Mar 10;11(1):26. doi: 10.1038/s41523-025-00738-7. NPJ Breast Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40064871 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rouzier R, Perou CM, Symmans WF, Ibrahim N, Cristofanilli M, Anderson K, et al. Breast cancer molecular subtypes respond differently to preoperative chemotherapy. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11:5678–85. - PubMed
-
- Carey LA, Dees EC, Sawyer L, Gatti L, Moore DT, Collichio F, et al. The triple negative paradox: primary tumor chemosensitivity of breast cancer subtypes. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13:2329–34. - PubMed
-
- Conforti R, Boulet T, Tomasic G, Taranchon E, Arriagada R, Spielmann M, et al. Breast cancer molecular subclassification and estrogen receptor expression to predict efficacy of adjuvant anthracyclines-based chemotherapy: a biomarker study from two randomized trials. Ann Oncol. 2007;18:1477–83. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

