IgG keeps virulent Salmonella from evading dendritic cell uptake
- PMID: 22352313
- PMCID: PMC3385029
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2012.03578.x
IgG keeps virulent Salmonella from evading dendritic cell uptake
Abstract
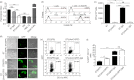
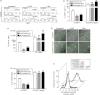
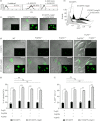
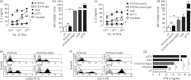
Dendritic cells (DCs) are phagocytic professional antigen-presenting cells that can prime naive T cells and initiate anti-bacterial immunity. However, several pathogenic bacteria have developed virulence mechanisms to impair DC function. For instance, Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium can prevent DCs from activating antigen-specific T cells. In addition, it has been described that the Salmonella Pathogenicity Island 1 (SPI-1), which promotes phagocytosis of bacteria in non-phagocytic cells, can suppress this process in DCs in a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) -dependent manner. Both mechanisms allow Salmonella to evade host adaptive immunity. Recent studies have shown that IgG-opsonization of Salmonella can restore the capacity of DCs to present antigenic peptide-MHC complexes and prime T cells. Interestingly, T-cell activation requires Fcγ receptor III (FcγRIII) expression over the DC surface, suggesting that this receptor could counteract both antigen presentation and phagocytosis evasion by bacteria. We show that, despite IgG-coated Salmonella retaining its capacity to secrete anti-capture proteins, DCs are efficiently capable of engulfing a large number of IgG-coated bacteria. These results suggest that DCs employ another mechanism to engulf IgG-coated Salmonella, different from that used for free bacteria. In this context, we noted that DCs do not employ PI3K, actin cytoskeleton or dynamin to capture IgG-coated bacteria. Likewise, we observed that the capture is an FcγR-independent mechanism. Interestingly, these internalized bacteria were rapidly targeted for degradation within lysosomal compartments. Hence, our results suggest a novel mechanism in DCs that does not employ PI3K/actin cytoskeleton/dynamin/FcγRs to engulf IgG-coated Salmonella, is not affected by anti-capture SPI-1-derived effectors and enhances DC immunogenicity, bacterial degradation and antigen presentation.
© 2012 The Authors. Immunology © 2012 Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Mechanisms used by virulent Salmonella to impair dendritic cell function and evade adaptive immunity.Immunology. 2012 Sep;137(1):28-36. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2012.03614.x. Immunology. 2012. PMID: 22703384 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Salmonella escape from antigen presentation can be overcome by targeting bacteria to Fc gamma receptors on dendritic cells.J Immunol. 2004 Sep 15;173(6):4058-65. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.173.6.4058. J Immunol. 2004. PMID: 15356155
-
Virulent Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium evades adaptive immunity by preventing dendritic cells from activating T cells.Infect Immun. 2006 Nov;74(11):6438-48. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00063-06. Infect Immun. 2006. PMID: 17057096 Free PMC article.
-
Immune complex-induced enhancement of bacterial antigen presentation requires Fcgamma receptor III expression on dendritic cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Aug 14;104(33):13402-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0700999104. Epub 2007 Aug 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17679697 Free PMC article.
-
Virulence mechanisms displayed by Salmonella to impair dendritic cell function.Curr Med Chem. 2010;17(12):1156-66. doi: 10.2174/092986710790827825. Curr Med Chem. 2010. PMID: 20158475 Review.
Cited by
-
Carbon monoxide exposure improves immune function in lupus-prone mice.Immunology. 2013 Sep;140(1):123-32. doi: 10.1111/imm.12124. Immunology. 2013. PMID: 23691924 Free PMC article.
-
Small Non-Coding RNAs: New Insights in Modulation of Host Immune Response by Intracellular Bacterial Pathogens.Front Immunol. 2016 Oct 18;7:431. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2016.00431. eCollection 2016. Front Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27803700 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms used by virulent Salmonella to impair dendritic cell function and evade adaptive immunity.Immunology. 2012 Sep;137(1):28-36. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2012.03614.x. Immunology. 2012. PMID: 22703384 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interactions of Salmonella enterica with dendritic cells.Virulence. 2012 Nov 15;3(7):660-7. doi: 10.4161/viru.22761. Epub 2012 Nov 15. Virulence. 2012. PMID: 23221476 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization and Evaluation of a Salmonella enterica Serotype Senftenberg Mutant Created by Deletion of Virulence-Related Genes for Use as a Live Attenuated Vaccine.Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2016 Oct 4;23(10):802-812. doi: 10.1128/CVI.00233-16. Print 2016 Oct. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27489135 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Banchereau J, Briere F, Caux C, Davoust J, Lebecque S, Liu YJ, Pulendran B, Palucka K. Immunobiology of dendritic cells. Annu Rev Immunol. 2000;18:767–811. - PubMed
-
- Ravetch JV. Fc receptors. Curr Opin Immunol. 1997;9:121–5. - PubMed
-
- Ravetch J. In vivo veritas: the surprising roles of Fc receptors in immunity. Nat Immunol. 2010;11:183–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

