Spatiotemporal neuronal correlates of seizure generation in focal epilepsy
- PMID: 22352423
- PMCID: PMC3339564
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1528-1167.2012.03417.x
Spatiotemporal neuronal correlates of seizure generation in focal epilepsy
Abstract
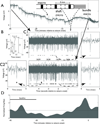
Purpose: Focal seizures are thought to reflect simultaneous activation of a large population of neurons within a discrete region of pathologic brain. Resective surgery targeting this focus is an effective treatment in carefully selected patients, but not all. Although in vivo recordings of single-neuron (i.e., "unit") activity in patients with epilepsy have a long history, no studies have examined long-term firing rates leading into seizures and the spatial relationship of unit activity with respect to the seizure-onset zone.
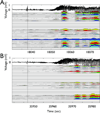
Methods: Microelectrode arrays recorded action potentials from neurons in mesial temporal structures (often including contralateral mesial temporal structures) in seven patients with mesial temporal lobe epilepsy.
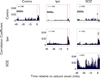
Key findings: Only 7.6% of microelectrode recordings showed increased firing rates before seizure onset and only 32.4% of microelectrodes showed any seizure-related activity changes. Surprisingly, firing rates on the majority of microelectrodes (67.6%) did not change throughout the seizure, including some microelectrodes located within the seizure-onset zone. Furthermore, changes in firing rate before and at seizure onset were observed on microelectrodes located outside the seizure-onset zone and even in contralateral mesial temporal lobe. These early changes varied from seizure to seizure, demonstrating the heterogeneity of ensemble activity underlying the generation of focal seizures. Increased neuronal synchrony was primarily observed only following seizure onset.
Significance: These results suggest that cellular correlates of seizure initiation and sustained ictal discharge in mesial temporal lobe epilepsy involve a small subset of the neurons within and outside the seizure-onset zone. These results further suggest that the "epileptic ensemble or network" responsible for seizure generation are more complex and heterogeneous than previously thought and that future studies may find mechanistic insights and therapeutic treatments outside the clinical seizure-onset zone.
Wiley Periodicals, Inc. © 2012 International League Against Epilepsy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest. We confirm that we have read the Journal’s position on issues involved in ethical publication and affirm that this report is consistent with those guidelines
Figures



References
-
- Aertsen AM, Gerstein G, Habib MK, Palm G. Dynamics of neuronal firing correlation: modulation of "effective connectivity". J Neurophysiol. 1989;61:900–917. - PubMed
-
- Babb TL, Crandall PH. Epileptogenesis of human limbic neurons in psychomotor epileptics. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1976;40:225–243. - PubMed
-
- Babb TL, Wilson CL, Isokawa-Akesson M. Firing patterns of human limbic neurons during stereoencephalography (SEEG) and clinical temporal lobe seizures. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1987;66:467–482. - PubMed
-
- Bower MR, Buckmaster PS. Changes in granule cell firing rates precede locally recorded spontaneous seizures by minutes in an animal model of temporal lobe epilepsy. J Neurophysiol. 2008;99:2431–2442. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

